nRF5 action!
-
Actually, there's another reason for wanting to avoid using the GPIO pins to intermediate waking up the MCU: earlier measurements in this thread showed that using the GPIO's in anything other than a "disconnected" state noticeably increases the current draw while sleeping.
-
@d00616 said in nRF5 Bluetooth action!:
Maybe someone has an idea about the reason. Here is my code for nRF5 and other with nRF24.
Now, I have the NRF5_ESB working under MY_CORE_ONLY condition. The HFCLK is not initialized. I do some code changes to allow using the radio in core only mode.
@d00616 said in nRF5 Bluetooth action!:
The HFCLK is not initialized.
Not sure if it helps you at all, but to save extra energy I'm using the PPI to turn-on HFCLK before the Rx "listen-mode" begins, and then turn it off after the receiver is subsequently put to sleep:
//Note: radio is assumed to be sleeping by this point, and with high frequency crystal oscillator turned off. NRF_PPI->CH[0].EEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RTC0->EVENTS_OVRFLW; //when COUNTER overflows. NRF_PPI->CH[0].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_CLOCK->TASKS_HFCLKSTART; //turn-on the HF crystal oscillator NRF_PPI->CH[1].EEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_CLOCK->EVENTS_HFCLKSTARTED; //After HF Clock started. NRF_PPI->CH[1].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RADIO->TASKS_RXEN; //turn on the radio receiver NRF_PPI->CH[2].EEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RADIO->EVENTS_READY; //After event READY, radio shall be in state RXIDLE. NRF_PPI->CH[2].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RADIO->TASKS_START; //Move from RXIDLE mode into RX mode. NRF_PPI->CH[3].EEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RTC0->EVENTS_COMPARE[0]; // If time to turn off the radio receiver NRF_PPI->CH[3].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RADIO->TASKS_STOP; //Move radio from RX mode back into RXIDLE mode NRF_PPI->CH[4].EEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RTC0->EVENTS_COMPARE[1]; // If enough time has passed NRF_PPI->CH[4].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RADIO->TASKS_DISABLE; //Sleep the radio NRF_PPI->FORK[4].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_CLOCK->TASKS_HFCLKSTOP; //Turn-off the high frequency crystal oscillator NRF_PPI->CH[5].EEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RTC0->EVENTS_COMPARE[2]; // If 100ms has passed NRF_PPI->CH[5].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RTC0->TASKS_TRIGOVRFLW; //Set COUNTER so that it will overflow in 16 ticks. NRF_PPI->CH[6].EEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RADIO->EVENTS_END; //packet received. NRF_PPI->CH[6].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_GPIOTE->TASKS_OUT[1]; //Make pin P0.18. be LOW (turn on the LED). NRF_PPI->CH[7].EEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_GPIOTE->EVENTS_IN[0]; //P0.16 pin change occured. NRF_PPI->CH[7].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_GPIOTE->TASKS_OUT[2]; //Make pin P0.17. be LOW (turn on the LED). NRF_PPI->CHENSET=B11111111; //enable Channels 7,6,5,4,3,2,1,and 0.It works. :)
-
Can you see any reason as to why the radio isn't waking the MCU after it receives a packet? Here's the entire sketch:
#include <nrf.h> //#include <MySensors.h> #include <RH_NRF51.h> // Singleton instance of the radio driver RH_NRF51 nrf51; bool toggle=true; uint32_t packetCounter=0; uint8_t myBuffer[20]; //required buffer for transmitting packet uint8_t my_default_network_address[] = {0xE7, 0xE7, 0xE7, 0xE7, 0xE7}; bool mySetNetworkAddress(uint8_t* address, uint8_t len) { if (len < 3 || len > 5) return false; // First byte is the prefix, remainder are base NRF_RADIO->PREFIX0 = ((address[0] << RADIO_PREFIX0_AP0_Pos) & RADIO_PREFIX0_AP0_Msk); uint32_t base; memcpy(&base, address+1, len-1); NRF_RADIO->BASE0 = base; NRF_RADIO->PCNF1 = ( (((sizeof(myBuffer)) << RADIO_PCNF1_MAXLEN_Pos) & RADIO_PCNF1_MAXLEN_Msk) // maximum length of payload | (((0UL) << RADIO_PCNF1_STATLEN_Pos) & RADIO_PCNF1_STATLEN_Msk) // expand the payload with 0 bytes | (((len-1) << RADIO_PCNF1_BALEN_Pos) & RADIO_PCNF1_BALEN_Msk)); // base address length in number of bytes. return true; } void myHwSleepPrepare(unsigned long ms) { // Idle serial device NRF_UART0->TASKS_STOPRX = 1; NRF_UART0->TASKS_STOPTX = 1; NRF_UART0->TASKS_SUSPEND = 1; //NRF_CLOCK->TASKS_HFCLKSTOP = 1; // Enable low power sleep mode NRF_POWER->TASKS_LOWPWR = 1; } // Sleep in System ON mode inline void doTheSleep() { __WFE(); __SEV(); __WFE(); } void myHwSleepEnd(unsigned long ms) { // Start HFCLK //if (nrf5_pwr_hfclk) { if (false) { NRF_CLOCK->EVENTS_HFCLKSTARTED = 0; NRF_CLOCK->TASKS_HFCLKSTART = 1; while (NRF_CLOCK->EVENTS_HFCLKSTARTED == 0) ; // Enable low latency sleep mode NRF_POWER->TASKS_CONSTLAT = 1; } // Start serial device //#ifndef MY_DISABLED_SERIAL NRF_UART0->TASKS_STARTRX = 1; NRF_UART0->TASKS_STARTTX = 1; //#endif } void myHwSleep(unsigned long ms) { myHwSleepPrepare(ms); doTheSleep(); //now sleeping myHwSleepEnd(ms); } void setup() { Serial.begin(250000); Serial.println(); Serial.println("Starting..."); Serial.flush(); NRF_POWER->DCDCEN=1; //enable the DCDC voltage regulator as the default. // Configure RTC NRF_RTC0->TASKS_STOP = 1; //stop the RTC counter so that it can be configured without incident // Enable interrupt //NVIC_SetPriority(GPIOTE_IRQn, 15); //NVIC_ClearPendingIRQ(GPIOTE_IRQn); //NVIC_EnableIRQ(GPIOTE_IRQn); NVIC_SetPriority(RADIO_IRQn, 15); NVIC_ClearPendingIRQ(RADIO_IRQn); NVIC_EnableIRQ(RADIO_IRQn); NRF_RADIO->INTENSET = B1000; //interrupt MCU if a packet is received. while (NRF_RADIO->INTENSET != B1000) {} //wait until confirmed //NRF_GPIOTE->INTENSET = 1; //interrupt MCU if change detected on pin P0.16. //while (NRF_GPIOTE->INTENSET != 1) {} //wait until confirmed Serial.print("LFCLKSTAT=0X"); Serial.print(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSTAT,HEX); Serial.print("=B"); Serial.println(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSTAT,BIN); Serial.flush(); NRF_RADIO->FREQUENCY=123; NRF_RADIO->MODE=1; //set 2Mbps datarate. NRF_RADIO->MODECNF0=1; //enable fast ramp-up of radio from DISABLED state. if (!nrf51.init()) Serial.println("init failed"); mySetNetworkAddress(my_default_network_address, sizeof(my_default_network_address)); if ((NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSTAT)>>2) {//if LF clock is running NRF_CLOCK->TASKS_LFCLKSTOP=1; //stop the clock while ((NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSTAT)& 1) {} //busy-wait until LF clock has stopped running Serial.println("LF clock is stopped."); } Serial.print("LFCLKSTAT=0x"); Serial.print(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSTAT,HEX); Serial.print("=B"); Serial.println(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSTAT,BIN); Serial.flush(); NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSRC=1; //use the crystal oscillator. while (!(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSRC=1)) {} // Serial.println("Crystal oscillator is now the LF choice."); Serial.print("LFCLKSTAT=0x"); Serial.print(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSTAT,HEX); Serial.print("=B"); Serial.println(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSTAT,BIN); Serial.flush(); NRF_CLOCK->TASKS_LFCLKSTART=1; //start the crystal oscillator clock while (!(NRF_CLOCK->EVENTS_LFCLKSTARTED)) {} //busy-wait until the clock is confirmed started. Serial.println("Low Frequency crystal oscillator started."); Serial.flush(); Serial.print("LFCLKSTAT=0x"); Serial.print(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSTAT,HEX); Serial.print("=B"); Serial.println(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSTAT,BIN); Serial.print("LFCLKSRC=0x"); Serial.print(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSRC,HEX); Serial.print("=B"); Serial.println(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSRC,BIN); Serial.print("Present PRESCALER="); Serial.println(NRF_RTC0->PRESCALER); Serial.print("LFCLKSTAT=0x"); Serial.print(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSTAT,HEX); Serial.print("=B"); Serial.println(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSTAT,BIN); NRF_RTC0->PRESCALER=0; //32768 frequency while (NRF_RTC0->PRESCALER!=0) {} //busy-wait until pre-scaler changes Serial.print("New PRESCALER="); Serial.println(NRF_RTC0->PRESCALER); Serial.println(); Serial.println("Finished setup."); Serial.flush(); //Radio enters RXIDLE soon after COUNTER overflows. NRF_RTC0->CC[0] = 24; //the time to exit RX state. NRF_RTC0->CC[1] = 25; //the time to put radio to sleep from RXIDLE NRF_RTC0->CC[2] = 3300; //the time to restart the cycle NRF_RTC0->EVENTS_COMPARE[0] = 0; //Clear the event flag. NRF_RTC0->EVENTS_COMPARE[1] = 0; //Clear the event flag. NRF_RTC0->EVENTS_COMPARE[2] = 0; //Clear the event flag. NRF_RADIO->TASKS_DISABLE=1; //sleep the radio while (NRF_RADIO->STATE) {}; //wait until radio is DISABLED (i.e. STATE=0); //Configure GPIOTE NRF_GPIOTE->CONFIG[0]=0x31001; // Toggle Event; Pin P0.16; Event Mode //So, any pin change on P0.16 will trigger an event. //On the Nordic nRF52 DK, Pin 0.16 is a button. NRF_GPIOTE->CONFIG[1]=0x131203; //Initial setting: HIGH; Toggle Task; Pin P0.18; Task Mode //On the Nordic nRF52 DK, Pin 0.18 is an LED. //Note: initial setting of HIGH means that the LED will be initially OFF. NRF_GPIOTE->CONFIG[2]=0x131103; //Initial setting: HIGH; Toggle Task; Pin P0.17; Task Mode //On the Nordic nRF52 DK, Pin P0.17 is an LED. //Note: initial setting of HIGH means that the LED will be initially OFF. //Note: radio is assumed to be sleeping by this point, and with high frequency crystal oscillator turned off. NRF_PPI->CH[0].EEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RTC0->EVENTS_OVRFLW; //when COUNTER overflows. NRF_PPI->CH[0].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_CLOCK->TASKS_HFCLKSTART; //turn on the HF crystal oscillator NRF_PPI->CH[1].EEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_CLOCK->EVENTS_HFCLKSTARTED; //After HF Clock started. NRF_PPI->CH[1].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RADIO->TASKS_RXEN; //turn on the radio receiver //NRF_PPI->FORK[1].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_GPIOTE->TASKS_OUT[0]; //Make pin P0.18. be HIGH NRF_PPI->CH[2].EEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RADIO->EVENTS_READY; //After event READY, radio shall be in state RXIDLE. NRF_PPI->CH[2].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RADIO->TASKS_START; //Move from RXIDLE mode into RX mode. NRF_PPI->CH[3].EEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RTC0->EVENTS_COMPARE[0]; // If time to turn off the radio receiver NRF_PPI->CH[3].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RADIO->TASKS_STOP; //Move radio from RX mode back into RXIDLE mode NRF_PPI->CH[4].EEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RTC0->EVENTS_COMPARE[1]; // If enough time has passed NRF_PPI->CH[4].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RADIO->TASKS_DISABLE; //Sleep the radio NRF_PPI->FORK[4].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_CLOCK->TASKS_HFCLKSTOP; //Turn off the high frequency crystal oscillator NRF_PPI->CH[5].EEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RTC0->EVENTS_COMPARE[2]; // If 100ms has passed NRF_PPI->CH[5].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RTC0->TASKS_TRIGOVRFLW; //Set COUNTER so that it will overflow in 16 ticks. NRF_PPI->CH[6].EEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RADIO->EVENTS_END; //packet received. NRF_PPI->CH[6].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_GPIOTE->TASKS_OUT[1]; //Make pin P0.18. be LOW (turn on the LED). NRF_PPI->CH[7].EEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_GPIOTE->EVENTS_IN[0]; //P0.16 pin change occured. NRF_PPI->CH[7].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_GPIOTE->TASKS_OUT[2]; //Make pin P0.17. be LOW (turn on the LED). NRF_PPI->CHENSET=B11111111; //enable Channels 7,6,5,4,3,2,1,and 0. NRF_CLOCK->TASKS_LFCLKSTART=1; //start the crystal oscillator clock while (!(NRF_CLOCK->EVENTS_LFCLKSTARTED)) {} //busy-wait until the clock is confirmed started. Serial.println("Crystal oscillator started."); Serial.flush(); NRF_RTC0->EVTENSET=0x70003; //enable routing of RTC TICK, OVRFLW, and comparison events to PPI for the comparisons while (NRF_RTC0->EVTEN!= (0x70003)) {}; //wait until EVTENSET setting is confirmed. NRF_RTC0->EVENTS_TICK=0; //clear TICKS flag NRF_RTC0->EVENTS_OVRFLW=0; //clear overflow flag NRF_RADIO->EVENTS_END=0; //clear payload received flag. NRF_CLOCK->TASKS_HFCLKSTOP=1; //Turn off the high frequency crystal oscillator. NRF_RTC0->TASKS_TRIGOVRFLW=1; //prepare COUNTER so that an overflow will ensue in 16 ticks. while (NRF_RTC0->COUNTER!=0xFFFFF0) {} //wait until COUNTER is primed to overflow. NRF_RTC0->TASKS_START=1; // Resume the RTC, which had been paused. while ((NRF_RTC0->EVENTS_TICK==0)) {} //wait until the radio is confirmed to be started. } uint32_t loopCounter=0; void loop() { Serial.print("time="); Serial.print(millis()); Serial.print(", packetCounter="); Serial.println(packetCounter); Serial.flush(); myHwSleep(500000000); //sleep 100ms. Already offset in setup by 1ms from wake-up of PPI. } // * Reset events and read back on nRF52 //* http://infocenter.nordicsemi.com/pdf/nRF52_Series_Migration_v1.0.pdf #if __CORTEX_M == 0x04 #define NRF5_RESET_EVENT(event) \ event = 0; \ (void)event #else #define NRF5_RESET_EVENT(event) event = 0 #endif // This must be in one line extern "C" { void RADIO_IRQHandler(void) {packetCounter++; NRF5_RESET_EVENT(NRF_RADIO->EVENTS_END); NRF_RADIO->EVENTS_END=0; }}The PPI does toggle an LED each time it receives a packet, but unfortunately the CPU remains asleep. Nonetheless, it does seem to follow your prescription for the ISR.
-
Can you see any reason as to why the radio isn't waking the MCU after it receives a packet? Here's the entire sketch:
#include <nrf.h> //#include <MySensors.h> #include <RH_NRF51.h> // Singleton instance of the radio driver RH_NRF51 nrf51; bool toggle=true; uint32_t packetCounter=0; uint8_t myBuffer[20]; //required buffer for transmitting packet uint8_t my_default_network_address[] = {0xE7, 0xE7, 0xE7, 0xE7, 0xE7}; bool mySetNetworkAddress(uint8_t* address, uint8_t len) { if (len < 3 || len > 5) return false; // First byte is the prefix, remainder are base NRF_RADIO->PREFIX0 = ((address[0] << RADIO_PREFIX0_AP0_Pos) & RADIO_PREFIX0_AP0_Msk); uint32_t base; memcpy(&base, address+1, len-1); NRF_RADIO->BASE0 = base; NRF_RADIO->PCNF1 = ( (((sizeof(myBuffer)) << RADIO_PCNF1_MAXLEN_Pos) & RADIO_PCNF1_MAXLEN_Msk) // maximum length of payload | (((0UL) << RADIO_PCNF1_STATLEN_Pos) & RADIO_PCNF1_STATLEN_Msk) // expand the payload with 0 bytes | (((len-1) << RADIO_PCNF1_BALEN_Pos) & RADIO_PCNF1_BALEN_Msk)); // base address length in number of bytes. return true; } void myHwSleepPrepare(unsigned long ms) { // Idle serial device NRF_UART0->TASKS_STOPRX = 1; NRF_UART0->TASKS_STOPTX = 1; NRF_UART0->TASKS_SUSPEND = 1; //NRF_CLOCK->TASKS_HFCLKSTOP = 1; // Enable low power sleep mode NRF_POWER->TASKS_LOWPWR = 1; } // Sleep in System ON mode inline void doTheSleep() { __WFE(); __SEV(); __WFE(); } void myHwSleepEnd(unsigned long ms) { // Start HFCLK //if (nrf5_pwr_hfclk) { if (false) { NRF_CLOCK->EVENTS_HFCLKSTARTED = 0; NRF_CLOCK->TASKS_HFCLKSTART = 1; while (NRF_CLOCK->EVENTS_HFCLKSTARTED == 0) ; // Enable low latency sleep mode NRF_POWER->TASKS_CONSTLAT = 1; } // Start serial device //#ifndef MY_DISABLED_SERIAL NRF_UART0->TASKS_STARTRX = 1; NRF_UART0->TASKS_STARTTX = 1; //#endif } void myHwSleep(unsigned long ms) { myHwSleepPrepare(ms); doTheSleep(); //now sleeping myHwSleepEnd(ms); } void setup() { Serial.begin(250000); Serial.println(); Serial.println("Starting..."); Serial.flush(); NRF_POWER->DCDCEN=1; //enable the DCDC voltage regulator as the default. // Configure RTC NRF_RTC0->TASKS_STOP = 1; //stop the RTC counter so that it can be configured without incident // Enable interrupt //NVIC_SetPriority(GPIOTE_IRQn, 15); //NVIC_ClearPendingIRQ(GPIOTE_IRQn); //NVIC_EnableIRQ(GPIOTE_IRQn); NVIC_SetPriority(RADIO_IRQn, 15); NVIC_ClearPendingIRQ(RADIO_IRQn); NVIC_EnableIRQ(RADIO_IRQn); NRF_RADIO->INTENSET = B1000; //interrupt MCU if a packet is received. while (NRF_RADIO->INTENSET != B1000) {} //wait until confirmed //NRF_GPIOTE->INTENSET = 1; //interrupt MCU if change detected on pin P0.16. //while (NRF_GPIOTE->INTENSET != 1) {} //wait until confirmed Serial.print("LFCLKSTAT=0X"); Serial.print(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSTAT,HEX); Serial.print("=B"); Serial.println(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSTAT,BIN); Serial.flush(); NRF_RADIO->FREQUENCY=123; NRF_RADIO->MODE=1; //set 2Mbps datarate. NRF_RADIO->MODECNF0=1; //enable fast ramp-up of radio from DISABLED state. if (!nrf51.init()) Serial.println("init failed"); mySetNetworkAddress(my_default_network_address, sizeof(my_default_network_address)); if ((NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSTAT)>>2) {//if LF clock is running NRF_CLOCK->TASKS_LFCLKSTOP=1; //stop the clock while ((NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSTAT)& 1) {} //busy-wait until LF clock has stopped running Serial.println("LF clock is stopped."); } Serial.print("LFCLKSTAT=0x"); Serial.print(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSTAT,HEX); Serial.print("=B"); Serial.println(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSTAT,BIN); Serial.flush(); NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSRC=1; //use the crystal oscillator. while (!(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSRC=1)) {} // Serial.println("Crystal oscillator is now the LF choice."); Serial.print("LFCLKSTAT=0x"); Serial.print(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSTAT,HEX); Serial.print("=B"); Serial.println(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSTAT,BIN); Serial.flush(); NRF_CLOCK->TASKS_LFCLKSTART=1; //start the crystal oscillator clock while (!(NRF_CLOCK->EVENTS_LFCLKSTARTED)) {} //busy-wait until the clock is confirmed started. Serial.println("Low Frequency crystal oscillator started."); Serial.flush(); Serial.print("LFCLKSTAT=0x"); Serial.print(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSTAT,HEX); Serial.print("=B"); Serial.println(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSTAT,BIN); Serial.print("LFCLKSRC=0x"); Serial.print(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSRC,HEX); Serial.print("=B"); Serial.println(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSRC,BIN); Serial.print("Present PRESCALER="); Serial.println(NRF_RTC0->PRESCALER); Serial.print("LFCLKSTAT=0x"); Serial.print(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSTAT,HEX); Serial.print("=B"); Serial.println(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSTAT,BIN); NRF_RTC0->PRESCALER=0; //32768 frequency while (NRF_RTC0->PRESCALER!=0) {} //busy-wait until pre-scaler changes Serial.print("New PRESCALER="); Serial.println(NRF_RTC0->PRESCALER); Serial.println(); Serial.println("Finished setup."); Serial.flush(); //Radio enters RXIDLE soon after COUNTER overflows. NRF_RTC0->CC[0] = 24; //the time to exit RX state. NRF_RTC0->CC[1] = 25; //the time to put radio to sleep from RXIDLE NRF_RTC0->CC[2] = 3300; //the time to restart the cycle NRF_RTC0->EVENTS_COMPARE[0] = 0; //Clear the event flag. NRF_RTC0->EVENTS_COMPARE[1] = 0; //Clear the event flag. NRF_RTC0->EVENTS_COMPARE[2] = 0; //Clear the event flag. NRF_RADIO->TASKS_DISABLE=1; //sleep the radio while (NRF_RADIO->STATE) {}; //wait until radio is DISABLED (i.e. STATE=0); //Configure GPIOTE NRF_GPIOTE->CONFIG[0]=0x31001; // Toggle Event; Pin P0.16; Event Mode //So, any pin change on P0.16 will trigger an event. //On the Nordic nRF52 DK, Pin 0.16 is a button. NRF_GPIOTE->CONFIG[1]=0x131203; //Initial setting: HIGH; Toggle Task; Pin P0.18; Task Mode //On the Nordic nRF52 DK, Pin 0.18 is an LED. //Note: initial setting of HIGH means that the LED will be initially OFF. NRF_GPIOTE->CONFIG[2]=0x131103; //Initial setting: HIGH; Toggle Task; Pin P0.17; Task Mode //On the Nordic nRF52 DK, Pin P0.17 is an LED. //Note: initial setting of HIGH means that the LED will be initially OFF. //Note: radio is assumed to be sleeping by this point, and with high frequency crystal oscillator turned off. NRF_PPI->CH[0].EEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RTC0->EVENTS_OVRFLW; //when COUNTER overflows. NRF_PPI->CH[0].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_CLOCK->TASKS_HFCLKSTART; //turn on the HF crystal oscillator NRF_PPI->CH[1].EEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_CLOCK->EVENTS_HFCLKSTARTED; //After HF Clock started. NRF_PPI->CH[1].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RADIO->TASKS_RXEN; //turn on the radio receiver //NRF_PPI->FORK[1].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_GPIOTE->TASKS_OUT[0]; //Make pin P0.18. be HIGH NRF_PPI->CH[2].EEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RADIO->EVENTS_READY; //After event READY, radio shall be in state RXIDLE. NRF_PPI->CH[2].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RADIO->TASKS_START; //Move from RXIDLE mode into RX mode. NRF_PPI->CH[3].EEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RTC0->EVENTS_COMPARE[0]; // If time to turn off the radio receiver NRF_PPI->CH[3].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RADIO->TASKS_STOP; //Move radio from RX mode back into RXIDLE mode NRF_PPI->CH[4].EEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RTC0->EVENTS_COMPARE[1]; // If enough time has passed NRF_PPI->CH[4].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RADIO->TASKS_DISABLE; //Sleep the radio NRF_PPI->FORK[4].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_CLOCK->TASKS_HFCLKSTOP; //Turn off the high frequency crystal oscillator NRF_PPI->CH[5].EEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RTC0->EVENTS_COMPARE[2]; // If 100ms has passed NRF_PPI->CH[5].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RTC0->TASKS_TRIGOVRFLW; //Set COUNTER so that it will overflow in 16 ticks. NRF_PPI->CH[6].EEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RADIO->EVENTS_END; //packet received. NRF_PPI->CH[6].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_GPIOTE->TASKS_OUT[1]; //Make pin P0.18. be LOW (turn on the LED). NRF_PPI->CH[7].EEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_GPIOTE->EVENTS_IN[0]; //P0.16 pin change occured. NRF_PPI->CH[7].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_GPIOTE->TASKS_OUT[2]; //Make pin P0.17. be LOW (turn on the LED). NRF_PPI->CHENSET=B11111111; //enable Channels 7,6,5,4,3,2,1,and 0. NRF_CLOCK->TASKS_LFCLKSTART=1; //start the crystal oscillator clock while (!(NRF_CLOCK->EVENTS_LFCLKSTARTED)) {} //busy-wait until the clock is confirmed started. Serial.println("Crystal oscillator started."); Serial.flush(); NRF_RTC0->EVTENSET=0x70003; //enable routing of RTC TICK, OVRFLW, and comparison events to PPI for the comparisons while (NRF_RTC0->EVTEN!= (0x70003)) {}; //wait until EVTENSET setting is confirmed. NRF_RTC0->EVENTS_TICK=0; //clear TICKS flag NRF_RTC0->EVENTS_OVRFLW=0; //clear overflow flag NRF_RADIO->EVENTS_END=0; //clear payload received flag. NRF_CLOCK->TASKS_HFCLKSTOP=1; //Turn off the high frequency crystal oscillator. NRF_RTC0->TASKS_TRIGOVRFLW=1; //prepare COUNTER so that an overflow will ensue in 16 ticks. while (NRF_RTC0->COUNTER!=0xFFFFF0) {} //wait until COUNTER is primed to overflow. NRF_RTC0->TASKS_START=1; // Resume the RTC, which had been paused. while ((NRF_RTC0->EVENTS_TICK==0)) {} //wait until the radio is confirmed to be started. } uint32_t loopCounter=0; void loop() { Serial.print("time="); Serial.print(millis()); Serial.print(", packetCounter="); Serial.println(packetCounter); Serial.flush(); myHwSleep(500000000); //sleep 100ms. Already offset in setup by 1ms from wake-up of PPI. } // * Reset events and read back on nRF52 //* http://infocenter.nordicsemi.com/pdf/nRF52_Series_Migration_v1.0.pdf #if __CORTEX_M == 0x04 #define NRF5_RESET_EVENT(event) \ event = 0; \ (void)event #else #define NRF5_RESET_EVENT(event) event = 0 #endif // This must be in one line extern "C" { void RADIO_IRQHandler(void) {packetCounter++; NRF5_RESET_EVENT(NRF_RADIO->EVENTS_END); NRF_RADIO->EVENTS_END=0; }}The PPI does toggle an LED each time it receives a packet, but unfortunately the CPU remains asleep. Nonetheless, it does seem to follow your prescription for the ISR.
-
@NeverDie
What if you activate a pin change interrupt/wake at the pin the PPI toggles?
Or connect it to another pin with pin change wake?@Uhrheber said in nRF5 Bluetooth action!:
@NeverDie
What if you activate a pin change interrupt/wake at the pin the PPI toggles?
Or connect it to another pin with pin change wake?Yes, I have tested that as a workaround. It "works", but using GPIO pins increases the current drain.
-
Well, I guess it's almost moot now, because I found and tested a better workaround. I re-wrote the PPI code so that after packet receipt, the PPI triggers an RTC0 overflow. It is that which is then used to wake-up the MCU. No GPIO pins need be involved, so no propagation delays and no increase in current drawn. It works.
I still think the radio ISR code (above) should have worked, but fortunately that's no longer holding me back now that I have a good enough workaround. :)
-
However, there's one fly in the ointment remaining. It turns out that some other timer is sometimes waking up the CPU:
time=15798, Radio STATE=0, COUNTER=0x49, packetCounter=22 time=15900, Radio STATE=0, COUNTER=0x49, packetCounter=23 time=16001, Radio STATE=0, COUNTER=0x49, packetCounter=24 time=16103, Radio STATE=0, COUNTER=0x49, packetCounter=25 time=16204, Radio STATE=0, COUNTER=0x49, packetCounter=26 time=16306, Radio STATE=0, COUNTER=0x49, packetCounter=27 time=512000, Radio STATE=0, COUNTER=0x2035, packetCounter=27 time=1024000, Radio STATE=0, COUNTER=0x269, packetCounter=27 time=1536000, Radio STATE=0, COUNTER=0x1803, packetCounter=27 time=2048000, Radio STATE=3, COUNTER=0x36, packetCounter=27 time=2560000, Radio STATE=0, COUNTER=0x1570, packetCounter=27 time=3072000, Radio STATE=0, COUNTER=0x3104, packetCounter=27 time=3584000, Radio STATE=0, COUNTER=0x1337, packetCounter=27 time=4096000, Radio STATE=0, COUNTER=0x2871, packetCounter=27 time=4608000, Radio STATE=0, COUNTER=0x1104, packetCounter=27 time=5120000, Radio STATE=0, COUNTER=0x2638, packetCounter=27All the lines labelled packetCounter=27 (after the first one that is) are a result of this. Looking at the time, they appear to happen on the rollover of some other timer (?)--apparently the one that is responsible for keeping track of millis(). I can filter them out after-the-fact, but I'd rather they not be waking up the CPU for no reason, as that is just a waste of energy.
-
Can you see any reason as to why the radio isn't waking the MCU after it receives a packet? Here's the entire sketch:
#include <nrf.h> //#include <MySensors.h> #include <RH_NRF51.h> // Singleton instance of the radio driver RH_NRF51 nrf51; bool toggle=true; uint32_t packetCounter=0; uint8_t myBuffer[20]; //required buffer for transmitting packet uint8_t my_default_network_address[] = {0xE7, 0xE7, 0xE7, 0xE7, 0xE7}; bool mySetNetworkAddress(uint8_t* address, uint8_t len) { if (len < 3 || len > 5) return false; // First byte is the prefix, remainder are base NRF_RADIO->PREFIX0 = ((address[0] << RADIO_PREFIX0_AP0_Pos) & RADIO_PREFIX0_AP0_Msk); uint32_t base; memcpy(&base, address+1, len-1); NRF_RADIO->BASE0 = base; NRF_RADIO->PCNF1 = ( (((sizeof(myBuffer)) << RADIO_PCNF1_MAXLEN_Pos) & RADIO_PCNF1_MAXLEN_Msk) // maximum length of payload | (((0UL) << RADIO_PCNF1_STATLEN_Pos) & RADIO_PCNF1_STATLEN_Msk) // expand the payload with 0 bytes | (((len-1) << RADIO_PCNF1_BALEN_Pos) & RADIO_PCNF1_BALEN_Msk)); // base address length in number of bytes. return true; } void myHwSleepPrepare(unsigned long ms) { // Idle serial device NRF_UART0->TASKS_STOPRX = 1; NRF_UART0->TASKS_STOPTX = 1; NRF_UART0->TASKS_SUSPEND = 1; //NRF_CLOCK->TASKS_HFCLKSTOP = 1; // Enable low power sleep mode NRF_POWER->TASKS_LOWPWR = 1; } // Sleep in System ON mode inline void doTheSleep() { __WFE(); __SEV(); __WFE(); } void myHwSleepEnd(unsigned long ms) { // Start HFCLK //if (nrf5_pwr_hfclk) { if (false) { NRF_CLOCK->EVENTS_HFCLKSTARTED = 0; NRF_CLOCK->TASKS_HFCLKSTART = 1; while (NRF_CLOCK->EVENTS_HFCLKSTARTED == 0) ; // Enable low latency sleep mode NRF_POWER->TASKS_CONSTLAT = 1; } // Start serial device //#ifndef MY_DISABLED_SERIAL NRF_UART0->TASKS_STARTRX = 1; NRF_UART0->TASKS_STARTTX = 1; //#endif } void myHwSleep(unsigned long ms) { myHwSleepPrepare(ms); doTheSleep(); //now sleeping myHwSleepEnd(ms); } void setup() { Serial.begin(250000); Serial.println(); Serial.println("Starting..."); Serial.flush(); NRF_POWER->DCDCEN=1; //enable the DCDC voltage regulator as the default. // Configure RTC NRF_RTC0->TASKS_STOP = 1; //stop the RTC counter so that it can be configured without incident // Enable interrupt //NVIC_SetPriority(GPIOTE_IRQn, 15); //NVIC_ClearPendingIRQ(GPIOTE_IRQn); //NVIC_EnableIRQ(GPIOTE_IRQn); NVIC_SetPriority(RADIO_IRQn, 15); NVIC_ClearPendingIRQ(RADIO_IRQn); NVIC_EnableIRQ(RADIO_IRQn); NRF_RADIO->INTENSET = B1000; //interrupt MCU if a packet is received. while (NRF_RADIO->INTENSET != B1000) {} //wait until confirmed //NRF_GPIOTE->INTENSET = 1; //interrupt MCU if change detected on pin P0.16. //while (NRF_GPIOTE->INTENSET != 1) {} //wait until confirmed Serial.print("LFCLKSTAT=0X"); Serial.print(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSTAT,HEX); Serial.print("=B"); Serial.println(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSTAT,BIN); Serial.flush(); NRF_RADIO->FREQUENCY=123; NRF_RADIO->MODE=1; //set 2Mbps datarate. NRF_RADIO->MODECNF0=1; //enable fast ramp-up of radio from DISABLED state. if (!nrf51.init()) Serial.println("init failed"); mySetNetworkAddress(my_default_network_address, sizeof(my_default_network_address)); if ((NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSTAT)>>2) {//if LF clock is running NRF_CLOCK->TASKS_LFCLKSTOP=1; //stop the clock while ((NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSTAT)& 1) {} //busy-wait until LF clock has stopped running Serial.println("LF clock is stopped."); } Serial.print("LFCLKSTAT=0x"); Serial.print(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSTAT,HEX); Serial.print("=B"); Serial.println(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSTAT,BIN); Serial.flush(); NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSRC=1; //use the crystal oscillator. while (!(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSRC=1)) {} // Serial.println("Crystal oscillator is now the LF choice."); Serial.print("LFCLKSTAT=0x"); Serial.print(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSTAT,HEX); Serial.print("=B"); Serial.println(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSTAT,BIN); Serial.flush(); NRF_CLOCK->TASKS_LFCLKSTART=1; //start the crystal oscillator clock while (!(NRF_CLOCK->EVENTS_LFCLKSTARTED)) {} //busy-wait until the clock is confirmed started. Serial.println("Low Frequency crystal oscillator started."); Serial.flush(); Serial.print("LFCLKSTAT=0x"); Serial.print(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSTAT,HEX); Serial.print("=B"); Serial.println(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSTAT,BIN); Serial.print("LFCLKSRC=0x"); Serial.print(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSRC,HEX); Serial.print("=B"); Serial.println(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSRC,BIN); Serial.print("Present PRESCALER="); Serial.println(NRF_RTC0->PRESCALER); Serial.print("LFCLKSTAT=0x"); Serial.print(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSTAT,HEX); Serial.print("=B"); Serial.println(NRF_CLOCK->LFCLKSTAT,BIN); NRF_RTC0->PRESCALER=0; //32768 frequency while (NRF_RTC0->PRESCALER!=0) {} //busy-wait until pre-scaler changes Serial.print("New PRESCALER="); Serial.println(NRF_RTC0->PRESCALER); Serial.println(); Serial.println("Finished setup."); Serial.flush(); //Radio enters RXIDLE soon after COUNTER overflows. NRF_RTC0->CC[0] = 24; //the time to exit RX state. NRF_RTC0->CC[1] = 25; //the time to put radio to sleep from RXIDLE NRF_RTC0->CC[2] = 3300; //the time to restart the cycle NRF_RTC0->EVENTS_COMPARE[0] = 0; //Clear the event flag. NRF_RTC0->EVENTS_COMPARE[1] = 0; //Clear the event flag. NRF_RTC0->EVENTS_COMPARE[2] = 0; //Clear the event flag. NRF_RADIO->TASKS_DISABLE=1; //sleep the radio while (NRF_RADIO->STATE) {}; //wait until radio is DISABLED (i.e. STATE=0); //Configure GPIOTE NRF_GPIOTE->CONFIG[0]=0x31001; // Toggle Event; Pin P0.16; Event Mode //So, any pin change on P0.16 will trigger an event. //On the Nordic nRF52 DK, Pin 0.16 is a button. NRF_GPIOTE->CONFIG[1]=0x131203; //Initial setting: HIGH; Toggle Task; Pin P0.18; Task Mode //On the Nordic nRF52 DK, Pin 0.18 is an LED. //Note: initial setting of HIGH means that the LED will be initially OFF. NRF_GPIOTE->CONFIG[2]=0x131103; //Initial setting: HIGH; Toggle Task; Pin P0.17; Task Mode //On the Nordic nRF52 DK, Pin P0.17 is an LED. //Note: initial setting of HIGH means that the LED will be initially OFF. //Note: radio is assumed to be sleeping by this point, and with high frequency crystal oscillator turned off. NRF_PPI->CH[0].EEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RTC0->EVENTS_OVRFLW; //when COUNTER overflows. NRF_PPI->CH[0].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_CLOCK->TASKS_HFCLKSTART; //turn on the HF crystal oscillator NRF_PPI->CH[1].EEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_CLOCK->EVENTS_HFCLKSTARTED; //After HF Clock started. NRF_PPI->CH[1].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RADIO->TASKS_RXEN; //turn on the radio receiver //NRF_PPI->FORK[1].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_GPIOTE->TASKS_OUT[0]; //Make pin P0.18. be HIGH NRF_PPI->CH[2].EEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RADIO->EVENTS_READY; //After event READY, radio shall be in state RXIDLE. NRF_PPI->CH[2].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RADIO->TASKS_START; //Move from RXIDLE mode into RX mode. NRF_PPI->CH[3].EEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RTC0->EVENTS_COMPARE[0]; // If time to turn off the radio receiver NRF_PPI->CH[3].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RADIO->TASKS_STOP; //Move radio from RX mode back into RXIDLE mode NRF_PPI->CH[4].EEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RTC0->EVENTS_COMPARE[1]; // If enough time has passed NRF_PPI->CH[4].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RADIO->TASKS_DISABLE; //Sleep the radio NRF_PPI->FORK[4].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_CLOCK->TASKS_HFCLKSTOP; //Turn off the high frequency crystal oscillator NRF_PPI->CH[5].EEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RTC0->EVENTS_COMPARE[2]; // If 100ms has passed NRF_PPI->CH[5].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RTC0->TASKS_TRIGOVRFLW; //Set COUNTER so that it will overflow in 16 ticks. NRF_PPI->CH[6].EEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_RADIO->EVENTS_END; //packet received. NRF_PPI->CH[6].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_GPIOTE->TASKS_OUT[1]; //Make pin P0.18. be LOW (turn on the LED). NRF_PPI->CH[7].EEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_GPIOTE->EVENTS_IN[0]; //P0.16 pin change occured. NRF_PPI->CH[7].TEP = (uint32_t)&NRF_GPIOTE->TASKS_OUT[2]; //Make pin P0.17. be LOW (turn on the LED). NRF_PPI->CHENSET=B11111111; //enable Channels 7,6,5,4,3,2,1,and 0. NRF_CLOCK->TASKS_LFCLKSTART=1; //start the crystal oscillator clock while (!(NRF_CLOCK->EVENTS_LFCLKSTARTED)) {} //busy-wait until the clock is confirmed started. Serial.println("Crystal oscillator started."); Serial.flush(); NRF_RTC0->EVTENSET=0x70003; //enable routing of RTC TICK, OVRFLW, and comparison events to PPI for the comparisons while (NRF_RTC0->EVTEN!= (0x70003)) {}; //wait until EVTENSET setting is confirmed. NRF_RTC0->EVENTS_TICK=0; //clear TICKS flag NRF_RTC0->EVENTS_OVRFLW=0; //clear overflow flag NRF_RADIO->EVENTS_END=0; //clear payload received flag. NRF_CLOCK->TASKS_HFCLKSTOP=1; //Turn off the high frequency crystal oscillator. NRF_RTC0->TASKS_TRIGOVRFLW=1; //prepare COUNTER so that an overflow will ensue in 16 ticks. while (NRF_RTC0->COUNTER!=0xFFFFF0) {} //wait until COUNTER is primed to overflow. NRF_RTC0->TASKS_START=1; // Resume the RTC, which had been paused. while ((NRF_RTC0->EVENTS_TICK==0)) {} //wait until the radio is confirmed to be started. } uint32_t loopCounter=0; void loop() { Serial.print("time="); Serial.print(millis()); Serial.print(", packetCounter="); Serial.println(packetCounter); Serial.flush(); myHwSleep(500000000); //sleep 100ms. Already offset in setup by 1ms from wake-up of PPI. } // * Reset events and read back on nRF52 //* http://infocenter.nordicsemi.com/pdf/nRF52_Series_Migration_v1.0.pdf #if __CORTEX_M == 0x04 #define NRF5_RESET_EVENT(event) \ event = 0; \ (void)event #else #define NRF5_RESET_EVENT(event) event = 0 #endif // This must be in one line extern "C" { void RADIO_IRQHandler(void) {packetCounter++; NRF5_RESET_EVENT(NRF_RADIO->EVENTS_END); NRF_RADIO->EVENTS_END=0; }}The PPI does toggle an LED each time it receives a packet, but unfortunately the CPU remains asleep. Nonetheless, it does seem to follow your prescription for the ISR.
@NeverDie said in nRF5 Bluetooth action!:
@d00616
Can you see any reason as to why the radio isn't waking the MCU after it receives a packet? Here's the entire sketch:I have no Idea why. The code is looking fine.
-
FWIW, I noticed on the oscilliscope that turning on-and-off the HFCLK ten times a second produces a fair amount of ringing. If I simply leave HFCLK turned on, most of the ringing is eliminated.
[Edit: So, if doing this as part of an aggressive energy saving approach (for instance, turning OFF HFCLK after RX mode and later turning it on again before initiating a new RX), what sort of extra circuitry beyond the two inductors for the DCDC might be needed? I don't know that the ringing is causing any actual problems, but it doesn't look proper on a scope. For now, I'm just flagging it so that folks are aware of it as a possible issue. ]
-
FWIW, I noticed on the oscilliscope that turning on-and-off the HFCLK ten times a second produces a fair amount of ringing. If I simply leave HFCLK turned on, most of the ringing is eliminated.
[Edit: So, if doing this as part of an aggressive energy saving approach (for instance, turning OFF HFCLK after RX mode and later turning it on again before initiating a new RX), what sort of extra circuitry beyond the two inductors for the DCDC might be needed? I don't know that the ringing is causing any actual problems, but it doesn't look proper on a scope. For now, I'm just flagging it so that folks are aware of it as a possible issue. ]
To better quantify the issue, I measured sleep currents (now using sleep routines that are a fork from what's in mysensors.h), and with the High Frequency clock turned OFF, the sleep current is measured at 2.2ua using a uCurrent Gold. However, the same setup, but with the High Frequency clock left ON, the sleep current is measured at 596ua using the same a uCurrent Gold.
So, clearly, for a battery/supercap application, leaving the High Frequency clock running all the time is not an especially good option.
-
To better quantify the issue, I measured sleep currents (now using sleep routines that are a fork from what's in mysensors.h), and with the High Frequency clock turned OFF, the sleep current is measured at 2.2ua using a uCurrent Gold. However, the same setup, but with the High Frequency clock left ON, the sleep current is measured at 596ua using the same a uCurrent Gold.
So, clearly, for a battery/supercap application, leaving the High Frequency clock running all the time is not an especially good option.
-
However, there's one fly in the ointment remaining. It turns out that some other timer is sometimes waking up the CPU:
time=15798, Radio STATE=0, COUNTER=0x49, packetCounter=22 time=15900, Radio STATE=0, COUNTER=0x49, packetCounter=23 time=16001, Radio STATE=0, COUNTER=0x49, packetCounter=24 time=16103, Radio STATE=0, COUNTER=0x49, packetCounter=25 time=16204, Radio STATE=0, COUNTER=0x49, packetCounter=26 time=16306, Radio STATE=0, COUNTER=0x49, packetCounter=27 time=512000, Radio STATE=0, COUNTER=0x2035, packetCounter=27 time=1024000, Radio STATE=0, COUNTER=0x269, packetCounter=27 time=1536000, Radio STATE=0, COUNTER=0x1803, packetCounter=27 time=2048000, Radio STATE=3, COUNTER=0x36, packetCounter=27 time=2560000, Radio STATE=0, COUNTER=0x1570, packetCounter=27 time=3072000, Radio STATE=0, COUNTER=0x3104, packetCounter=27 time=3584000, Radio STATE=0, COUNTER=0x1337, packetCounter=27 time=4096000, Radio STATE=0, COUNTER=0x2871, packetCounter=27 time=4608000, Radio STATE=0, COUNTER=0x1104, packetCounter=27 time=5120000, Radio STATE=0, COUNTER=0x2638, packetCounter=27All the lines labelled packetCounter=27 (after the first one that is) are a result of this. Looking at the time, they appear to happen on the rollover of some other timer (?)--apparently the one that is responsible for keeping track of millis(). I can filter them out after-the-fact, but I'd rather they not be waking up the CPU for no reason, as that is just a waste of energy.
This post is deleted! -
@NeverDie
I am puzzled with your 596ua?
I thought you were under 10ua with the mysensors sleep some time ago?
Mine only measures 4-5ua when in sleep?@rmtucker said in nRF5 Bluetooth action!:
I am puzzled with your 596ua?
I thought you were under 10ua with the mysensors sleep some time ago?There's no contradiction. It's a different scenario. The MySensors hwSleep function turns off the High Frequency oscillator when sleeping and turns it back on when it wakes up. So, it's perfectly fine for sleeping your device, having it wake up to send something, and then go back to sleep.
The present scenario that I'm working on though is where the MCU sleeps and the PPI manages a "listen mode" where the PPI wakes up the radio once every 100ms for a roughly 200us window of time to listen for an incoming packet. Then it goes back to sleep if nothing is received. On the other hand, if a packet is received, it wakes up the MCU so that the packet can be read and dealt with. Presently I have the PPI turn off the high-frequency oscillator each time after it has finished RX in the listen-mode cycle. Before entering RX again to listen for a new packet, it first ramps up the high frequency oscillator. According to the datasheet, the high frequency crystal oscillator must be operating in order for the radio to either transmit or receive. i.e. it can't simply run off the high frequency RC oscillator the way the MCU can.
My measurements show that while the High Frequency oscillator is running, it consumes about 596ua.
-
Did anyone managed to get two NRF52832 to connect to each other with the arduino IDE and communicate?
Also why does I2C initializes only after an SWD programmed gets connected?
Wierd phenomenon when I use an I2C oled display with that chip and program it with an st link V2 after it displays alright when it's booted if the SWD programmer is connected but as soon as you disconnect it everything else works but the I2C display...
-
Did anyone managed to get two NRF52832 to connect to each other with the arduino IDE and communicate?
Also why does I2C initializes only after an SWD programmed gets connected?
Wierd phenomenon when I use an I2C oled display with that chip and program it with an st link V2 after it displays alright when it's booted if the SWD programmer is connected but as soon as you disconnect it everything else works but the I2C display...
@Mike_Lemo said in nRF5 Bluetooth action!:
Did anyone managed to get two NRF52832 to connect to each other with the arduino IDE and communicate?
Yes. @d00616's demo code will do this.
I don't know the answers to the rest of your questions, because I don't use the ST.
-
Here's a scopeshot of how the revised current draw looks:
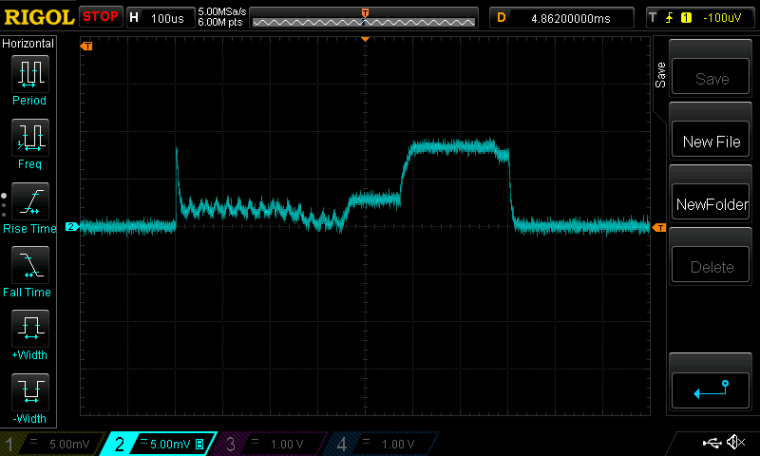
As you can see, there is now about a 370us warm-up time at the beginning for the High Frequency oscillator to come up to speed before the RX cycle can be started. Then it takes about 100us for the receiver to warm-up to RXIDLE. From there it finally achieves about 200us of actual productive RX time. Then everything powers down until the end of the 100ms cycle, after which it all repeats again. To conserve energy, all this is managed by the PPI while the MCU sleeps.
Scale: 1mv=1maI think this is about as energy efficient as it's ever going to get, short of chipping away at the number of bits in the frame/packet size, as I indicated earlier.
-
@Mike_Lemo said in nRF5 Bluetooth action!:
Did anyone managed to get two NRF52832 to connect to each other with the arduino IDE and communicate?
Yes. @d00616's demo code will do this.
I don't know the answers to the rest of your questions, because I don't use the ST.
@NeverDie said in nRF5 Bluetooth action!:
@Mike_Lemo said in nRF5 Bluetooth action!:
Did anyone managed to get two NRF52832 to connect to each other with the arduino IDE and communicate?Yes. @d00616's demo code will do this.
I don't know the answers to the rest of your questions, because I don't use the ST.
Any idea how I reach to this code?
Also you say you don't experience any issues with I2C like that?
-
@NeverDie said in nRF5 Bluetooth action!:
@Mike_Lemo said in nRF5 Bluetooth action!:
Did anyone managed to get two NRF52832 to connect to each other with the arduino IDE and communicate?Yes. @d00616's demo code will do this.
I don't know the answers to the rest of your questions, because I don't use the ST.
Any idea how I reach to this code?
Also you say you don't experience any issues with I2C like that?
@Mike_Lemo said in nRF5 Bluetooth action!:
Any idea how I reach to this code?
Yes, it's all explained in detail by @d00616 here: https://www.openhardware.io/view/376/MySensors-NRF5-Platform
Also you say you don't experience any issues with I2C like that?
Haven't tried I2C on this platform yet. I'd be very surprised if it didn't work though, as that's ARM Cortex M4 stuff, which is well vetted. i.e. no real dependency on anything Nordic per se.
-
@Mike_Lemo said in nRF5 Bluetooth action!:
Any idea how I reach to this code?
Yes, it's all explained in detail by @d00616 here: https://www.openhardware.io/view/376/MySensors-NRF5-Platform
Also you say you don't experience any issues with I2C like that?
Haven't tried I2C on this platform yet. I'd be very surprised if it didn't work though, as that's ARM Cortex M4 stuff, which is well vetted. i.e. no real dependency on anything Nordic per se.
@NeverDie said in nRF5 Bluetooth action!:
@Mike_Lemo said in nRF5 Bluetooth action!:
Any idea how I reach to this code?
Yes, it's all explained in detail by @d00616 here: https://www.openhardware.io/view/376/MySensors-NRF5-Platform
Also you say you don't experience any issues with I2C like that?
Haven't tried I2C on this platform yet. I'd be very surprised if it didn't work though, as that's ARM Cortex M4 stuff, which is well vetted. i.e. no real dependency on anything Nordic per se.
The link you attached links me to a getting started page not wireing two nrf's together
-
@NeverDie said in nRF5 Bluetooth action!:
@Mike_Lemo said in nRF5 Bluetooth action!:
Any idea how I reach to this code?
Yes, it's all explained in detail by @d00616 here: https://www.openhardware.io/view/376/MySensors-NRF5-Platform
Also you say you don't experience any issues with I2C like that?
Haven't tried I2C on this platform yet. I'd be very surprised if it didn't work though, as that's ARM Cortex M4 stuff, which is well vetted. i.e. no real dependency on anything Nordic per se.
The link you attached links me to a getting started page not wireing two nrf's together
@Mike_Lemo said in nRF5 Bluetooth action!:
The link you attached links me to a getting started page not wireing two nrf's together
Your question was ambiguous. When you said "connect" I just assumed you meant wirelessly connect.
Sorry, I can't help you. Seems like @scalz has gotten I2C to work with it though, but more likely for reading a TH sensor than for the purpose of wiring two nRF52832's. Still, that would prove that it works. If you know the I2C protocol, it shouldn't be hard to go from that to wiring two nRF52832's together.
