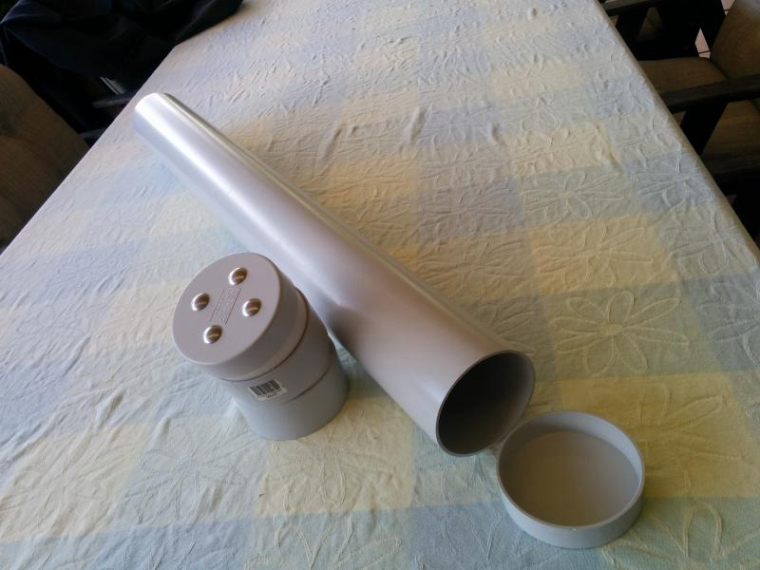
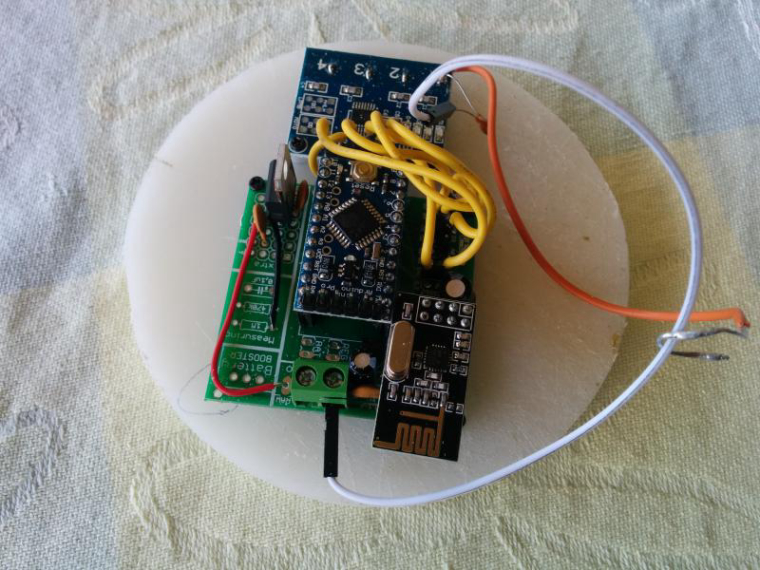
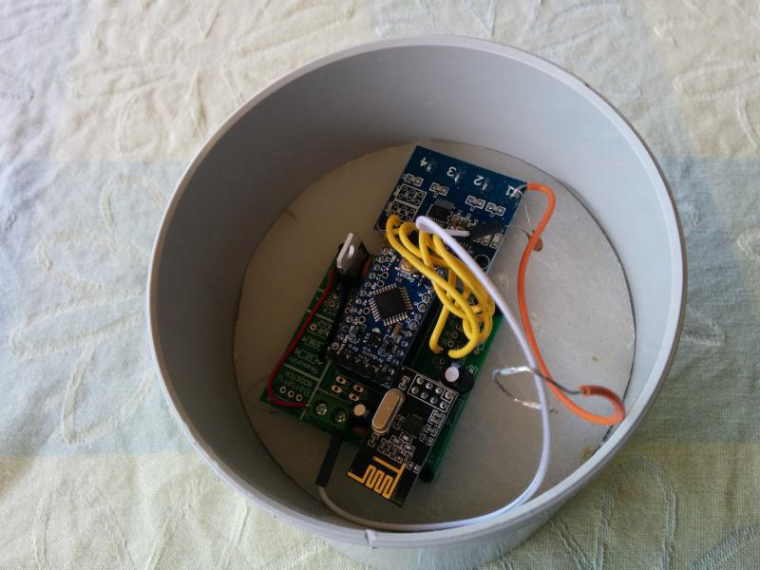
Hi
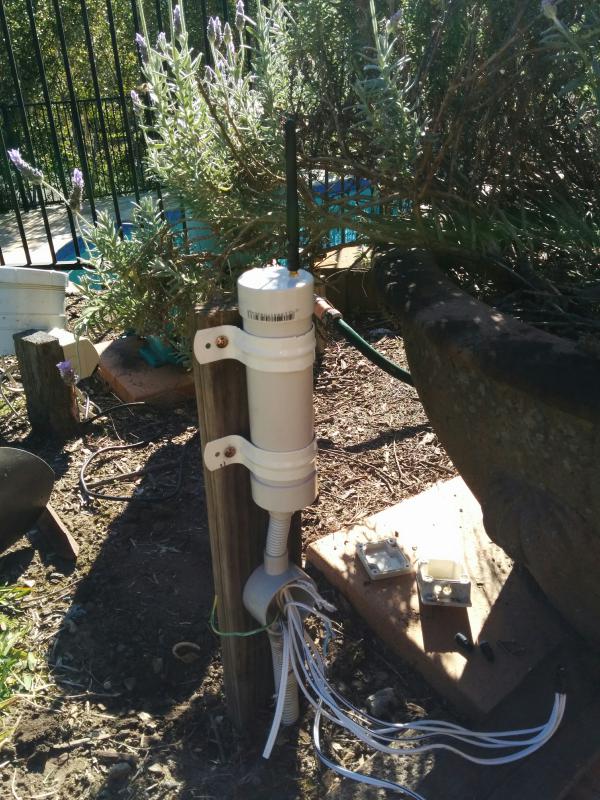
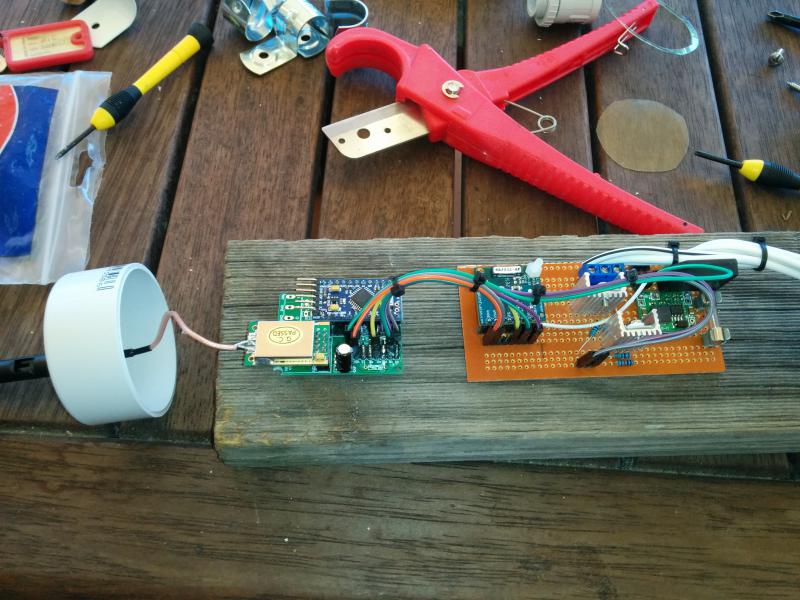
I have installed a node to monitor our 12v auxiliary supply for our home. The power system consists of a 200w panel on the roof and a 105AH battery located in our server cabinet. When we built our home I ran a 12v Backbone as well so we can access the low voltage power all over . To date it has been used to run a system of night lights and reading lamps but now that I have found Mysensors I hope it will soon be powering a lot more :) .
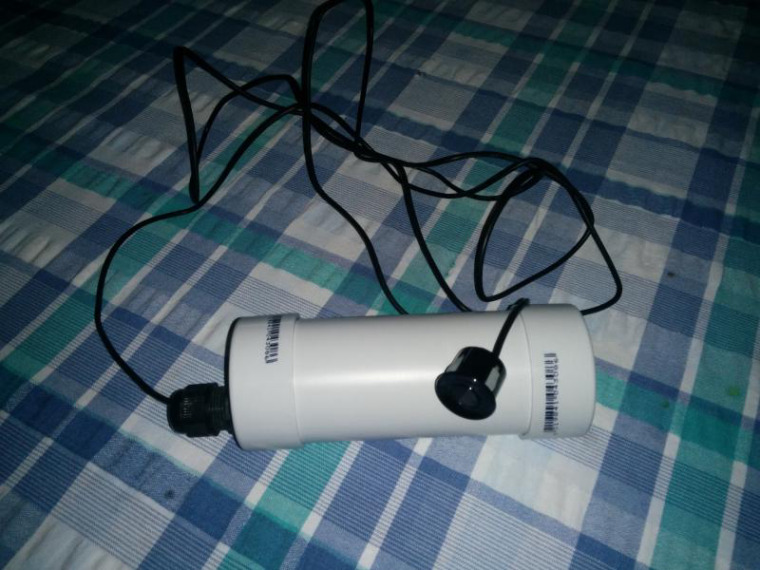
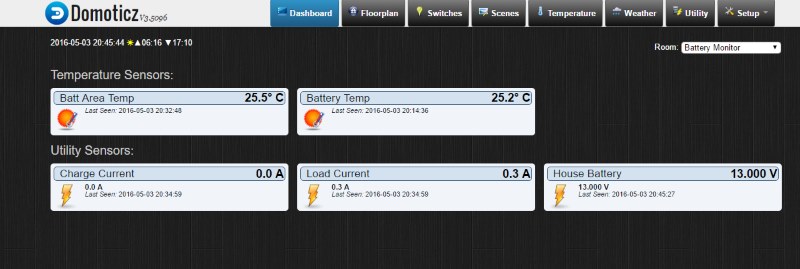
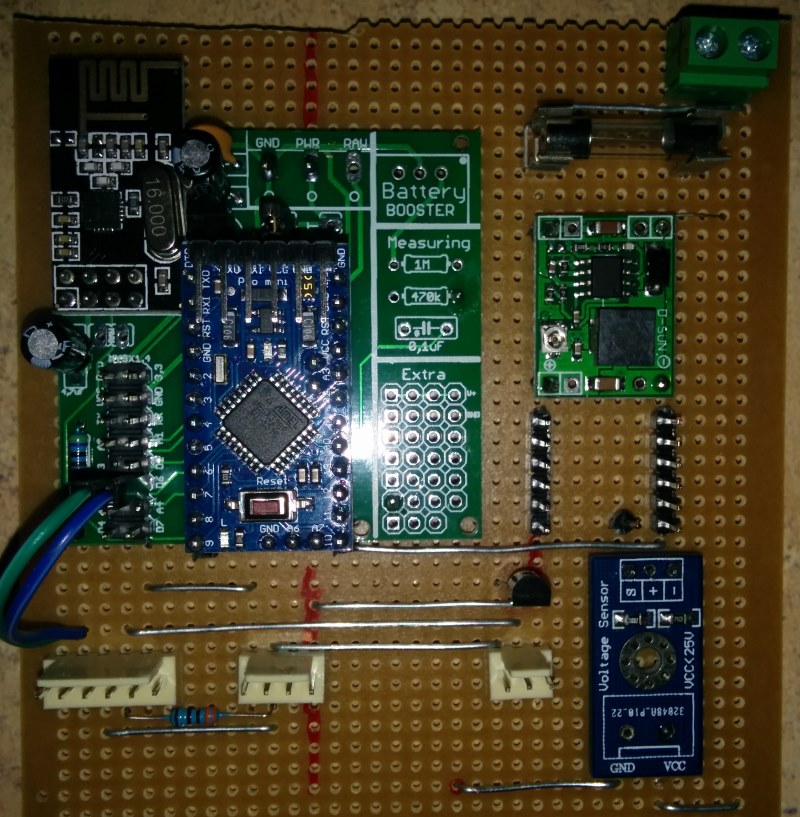
Ok this node has been running for a few weeks now so thought i would share it with others. it monitors battery voltage, Charge current, Dis-charge current, Ambient temp and battery Temp. I have included the temperature monitors after a friend had his battery develop an internal short and melt in his caravan, not a pretty sight.
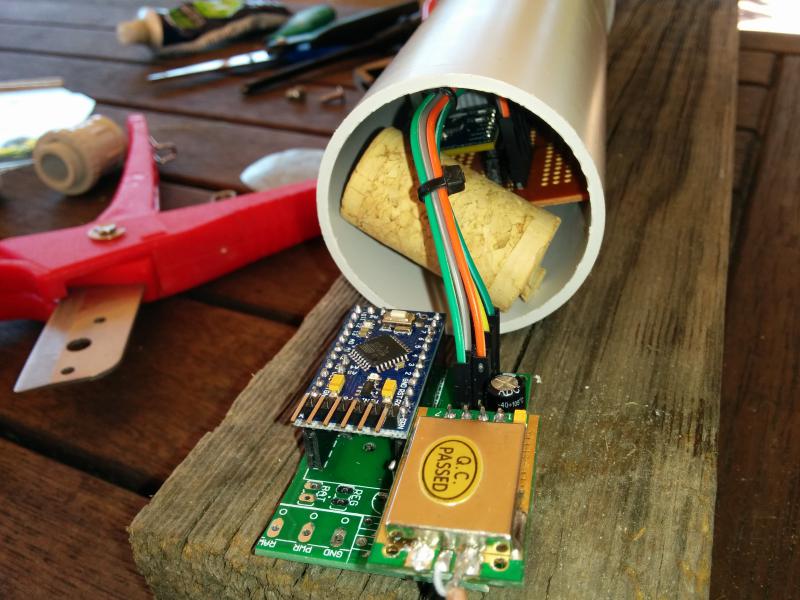
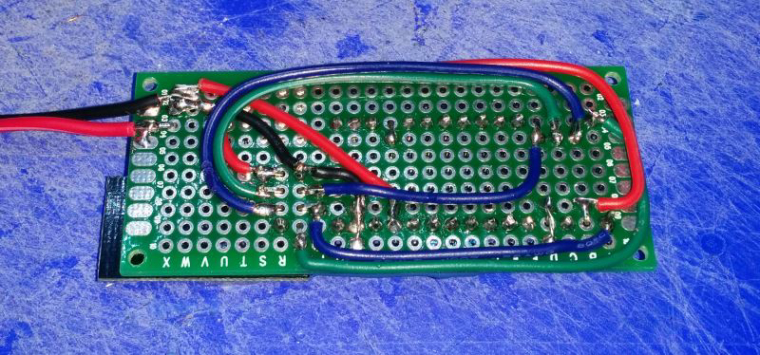
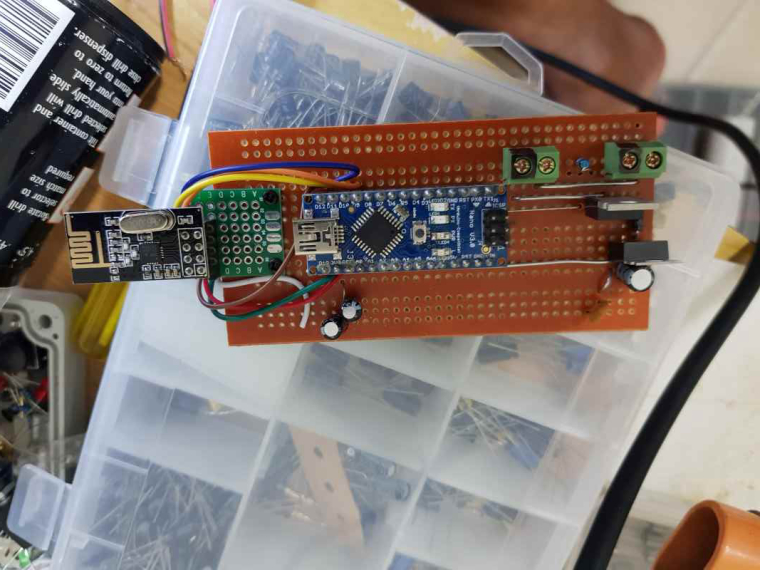
My notes are based on my breadboard version which was built around an Arduino nano, In the final I used a Pro Mini.
Parts List:
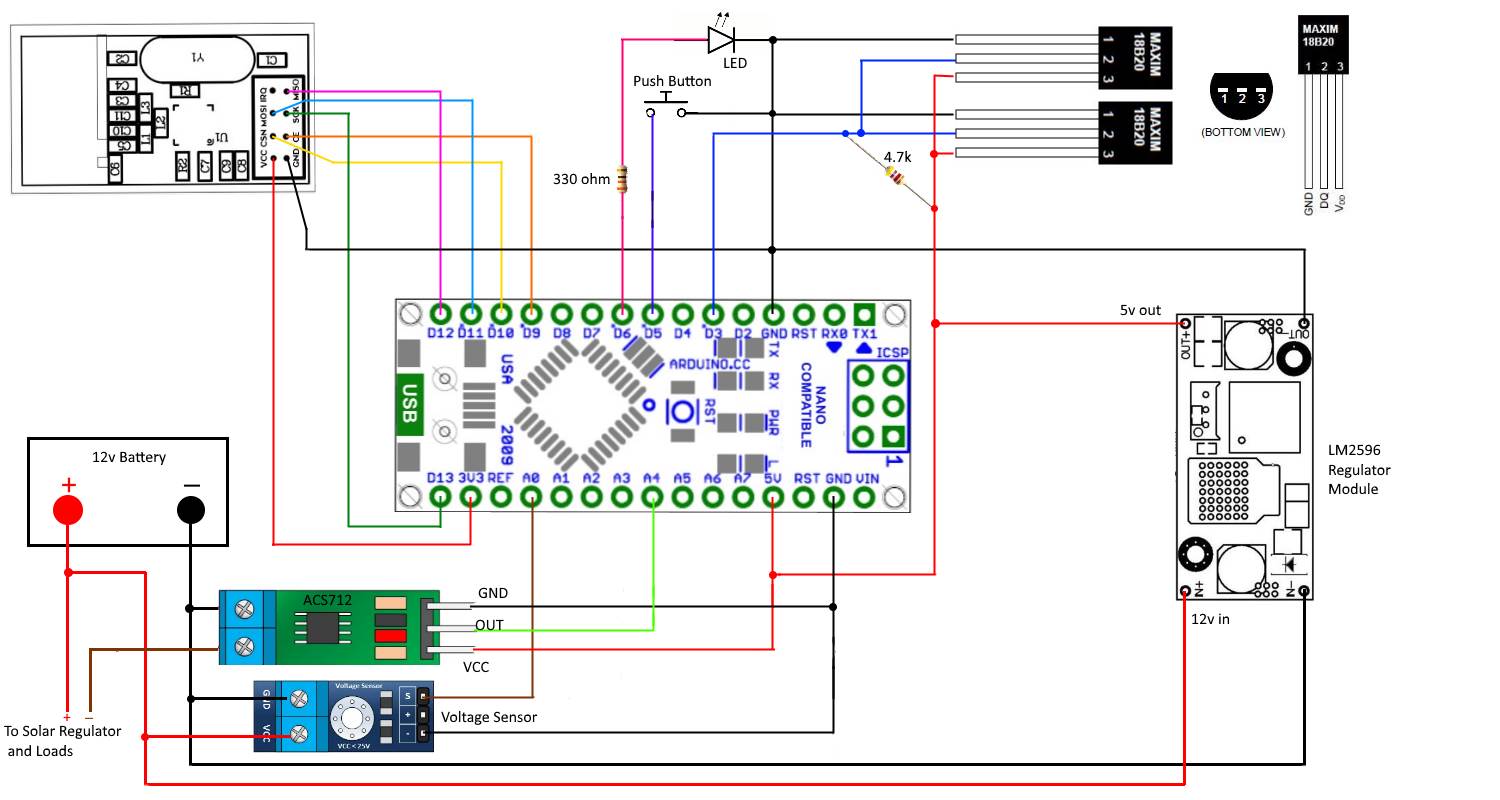
1 x Arduino I have used a Nano but other types or OK too
1 x ACS712 Current sensing Module. These are available in 5A, 20A and 30A. Choose whichever current fills your needs. Only one line of code needs to be modified to suit your selected device.
2 x DS18b20 Temperature sensors
1 x Voltage sensing module or 2 x resistors to be used as a voltage divider. I have used a module that has a maximum reading of 25v. That means when the module sees 25v on its input the output of the module will be 5v.
1 x nRF24L01+ 2.4ghz Transceiver
1 x LM2596 regulator module or some other regulator able to supply 5v
1x 330 ohm resistor
1x 4.7 k ohm resistor
1x LED
1x push button
When using the analog inputs of the Arduino it is very important that you have a very stable 5v supply voltage. The 20A ACS712 shows a change of only 100mv for every 1A so you can see even small fluctuations can cause sizable errors in your readings. During construction I found powering the circuit from the usb port to give unreliable results and opted for a dedicated 5v supply instead.
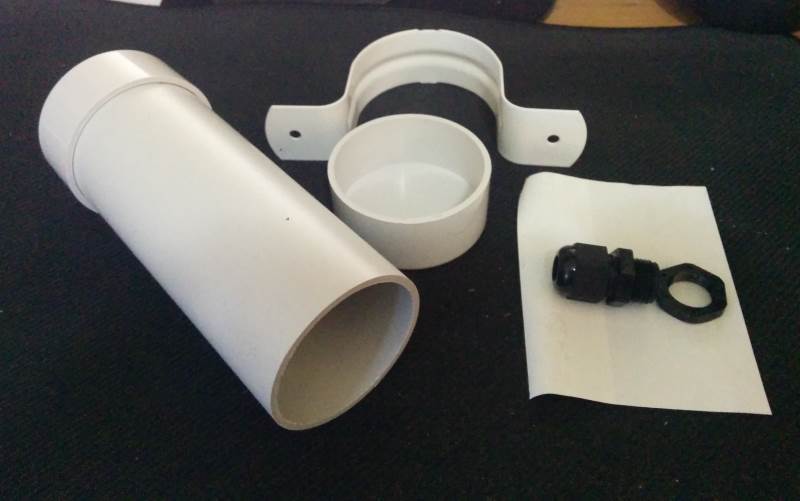
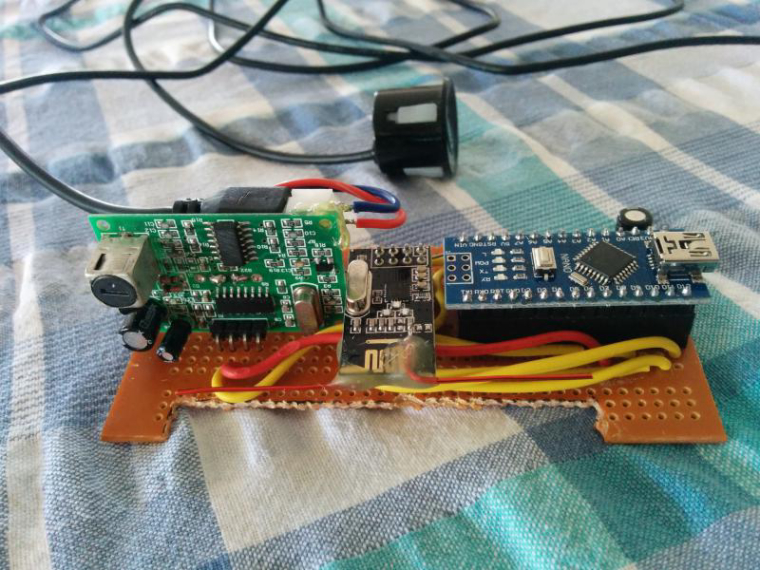
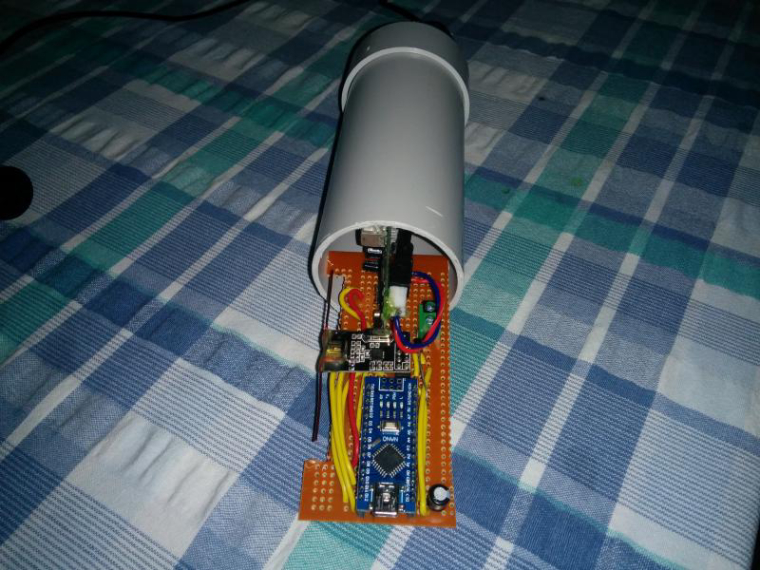
Construction:
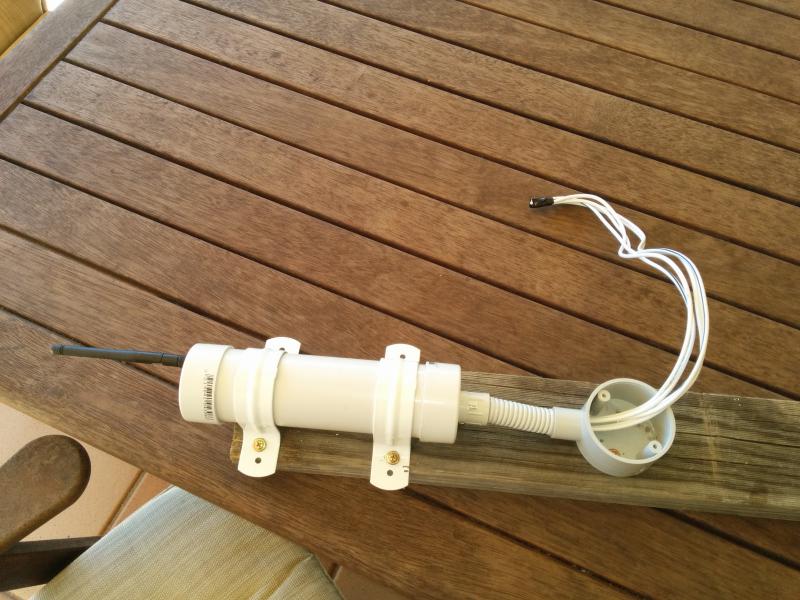
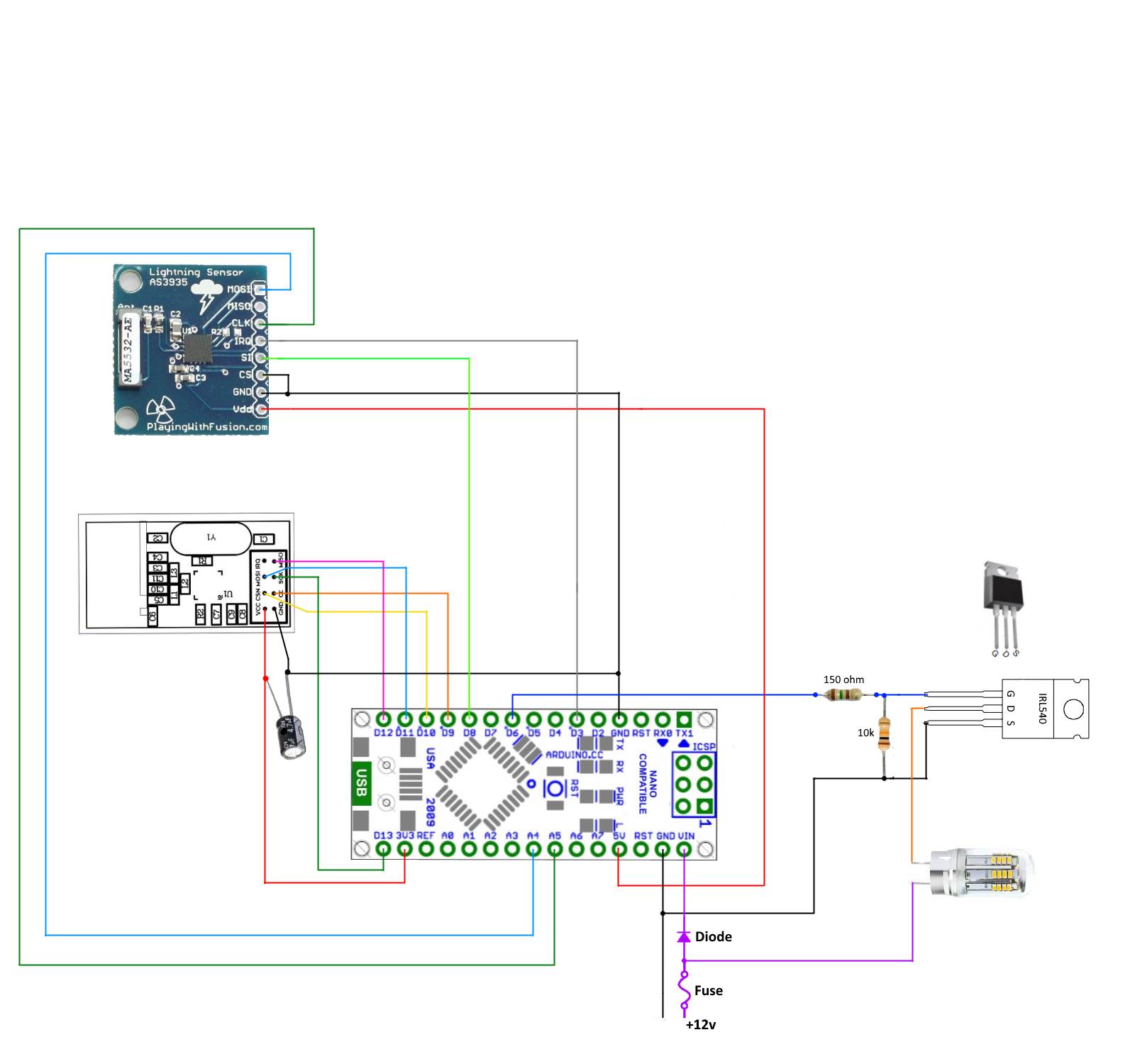
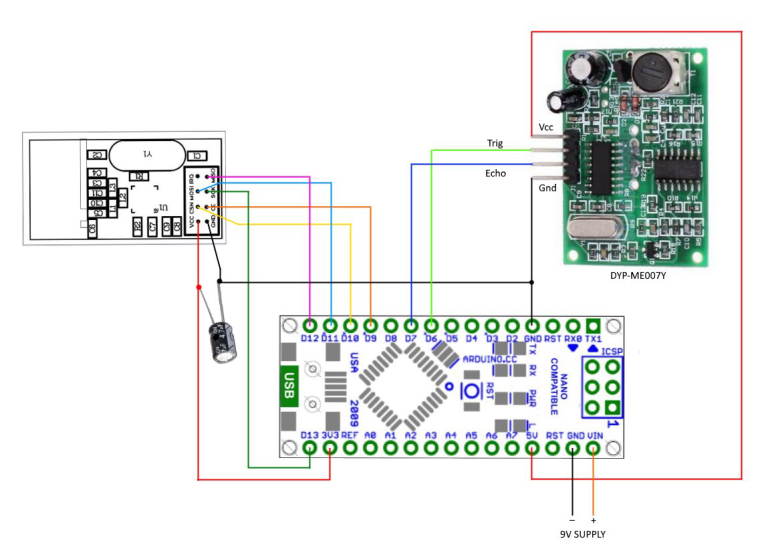
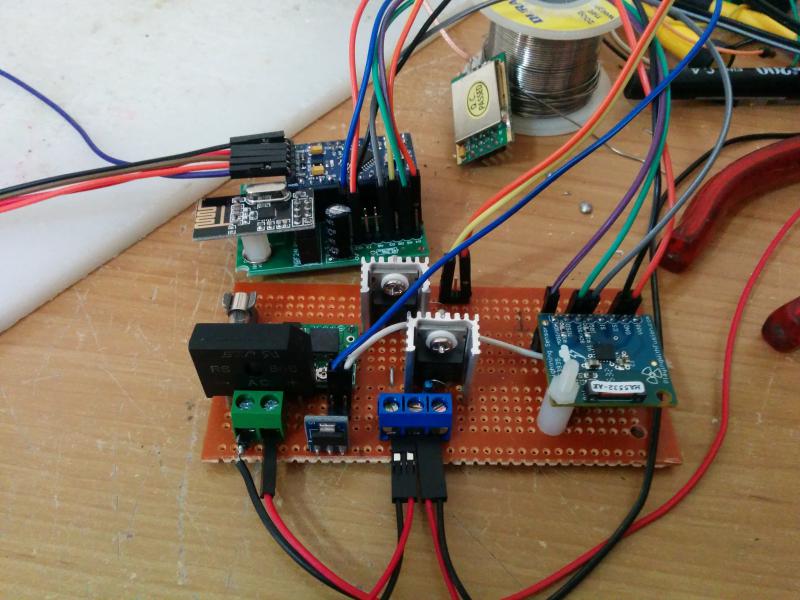
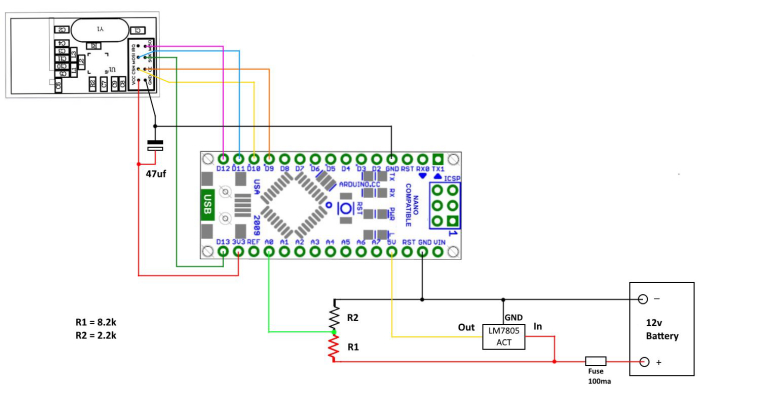
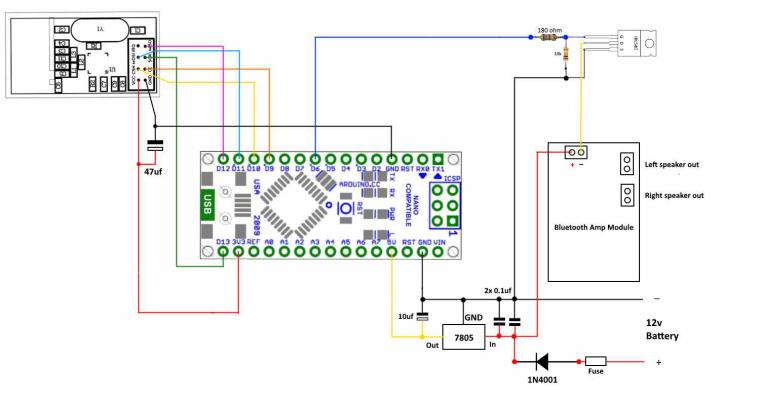
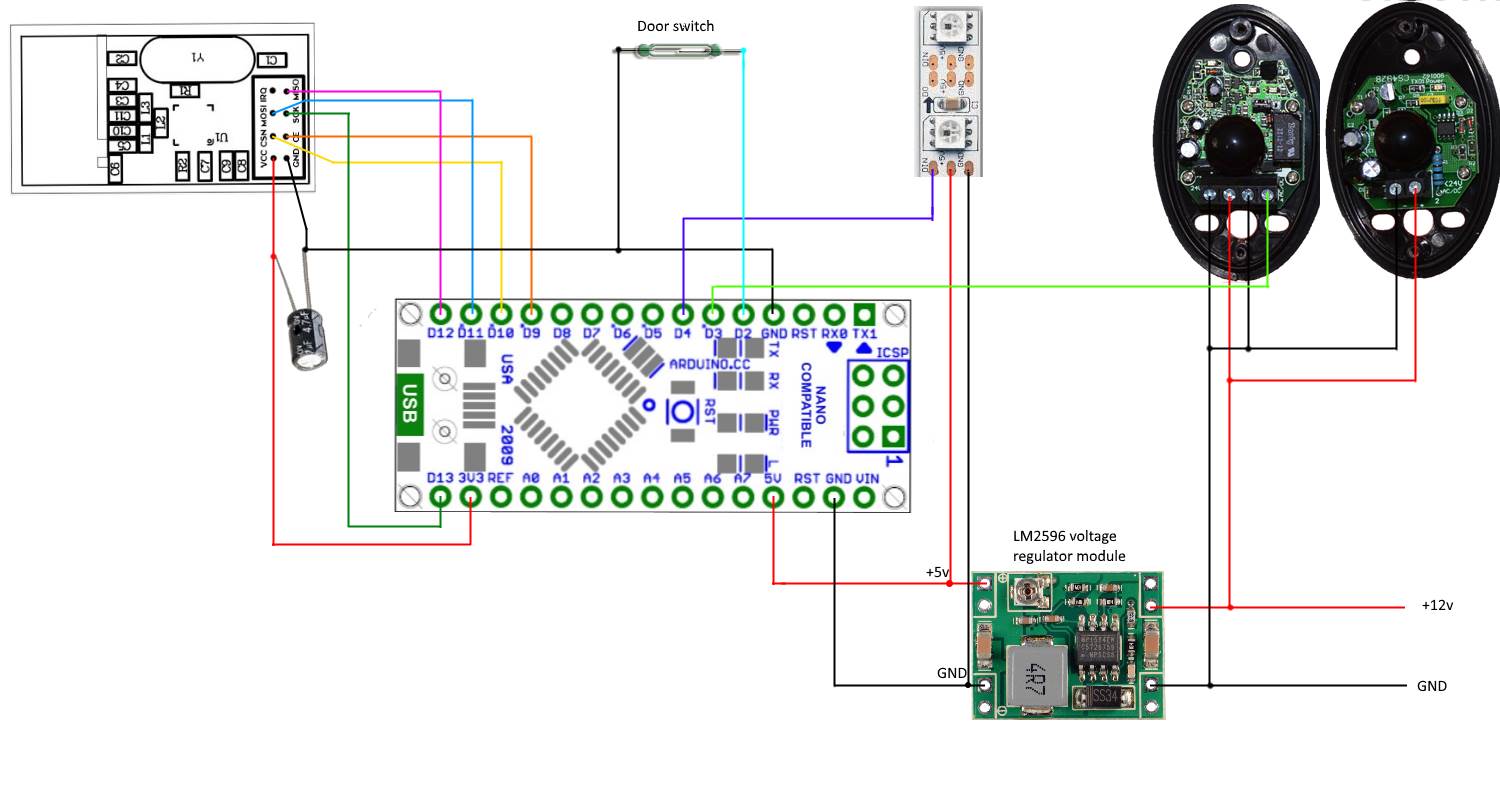
Wire the devices as shown below.
The Sketch:
/*Sketch for a MySensor node to monitor a 12v battery with a solar panel for charging
* The node monitors battery voltage,current into and out of the battery, ambient temperature and battery temperature.
* 2 x DS18b20 dallas temperature ic's their data pins connected to arduino digital pin 3
* 1 x ACS712 current sensor module connected to arduino analog pin A4
* 1 x 25v voltage sensor module connected to arduino analog pin A0
* 1 x nRF24L01+ 2.4ghz tranceiver connected as per the MySensors web site.
* 1 x LED connected via a 330 ohm resistor to pin 6
* 1 x push button connected to pin 5
*/
#include <MySensor.h>
#include <SPI.h>
#include <OneWire.h>
#include <DallasTemperature.h>
#define ONE_WIRE_BUS 3 // Ds18b20 data wire is connected to digital pin 3 on the Arduino
#define ID_S_TEMPA 0 // First temp device
#define ID_S_TEMPB 1 // second temp device
#define ID_S_MULTIMETERV 3 // Multimeter device for voltage measurement
#define ID_S_MULTIMETERC 4 // Multimeter device for positive current measurement
#define ID_S_MULTIMETERC1 5 // Multimeter device for negative current measurement
#define NUM_SAMPLES 10 // number of analog voltage samples to take per reading
int ledPin = 6; // the pin for the LED
int buttonPin = 5; // the input pin for offset pushbutton
int buttonState = 0; // variable for reading the pin status
unsigned long SLEEP_TIME = 30000; // Sleep time between reads (in milliseconds)
int lastmilli = 25000; // set to an arbitary number outside of expected current sensor range to ensure a change when first run
float sensitivity = 100 ; //change this to 185 for ACS712-5 or to 100 for ACS712-20A or to 66 for ACS712-30A
int VQ = 0; //Placeholder for quiescent voltage calculations
int ACSPin = A4; // Analog pin number the ACS712 data pin connects to
float lastTemperature[2]; //Array to hold the last temp readings sent to gateway, only send new data if different
int sum = 0; // sum of voltage samples taken
unsigned char sample_count = 0; // current sample number
int lastVoltage = 30000; // set to an arbitary number outside of expected voltage sensor range to ensure a change when first run
int voltagePin = A0; // analog pin voltage sensor or voltage divider is connected to
int voltSenseMax = 25000; // set to the maximum input voltage in millivolts of your voltage divider input
OneWire oneWire(ONE_WIRE_BUS); // Setup a oneWire instance to communicate with any OneWire devices (not just Maxim/Dallas temperature ICs)
DallasTemperature sensors(&oneWire); // Pass our oneWire reference to Dallas Temperature.
MySensor gw;
// ------ Initialize messages -------
MyMessage msg(0,V_TEMP);
MyMessage msg_S_MULTIMETERv(ID_S_MULTIMETERV,V_VOLTAGE);
MyMessage msg_S_MULTIMETERc(ID_S_MULTIMETERC,V_CURRENT);
MyMessage msg_S_MULTIMETERc1(ID_S_MULTIMETERC1,V_CURRENT);
void setup()
{
sensors.begin(); // Start up the onewire library
gw.begin(); // Startup and initialize MySensors library. Set callback for incoming messages.
gw.sendSketchInfo("Battery Status Sensor", "1"); // Send the sketch version information to the gateway and Controller
// ------ Present all sensors to controller ------
gw.present(ID_S_TEMPA, S_TEMP);
gw.present(ID_S_TEMPB, S_TEMP);
gw.present(ID_S_MULTIMETERV,V_VOLTAGE);
gw.present(ID_S_MULTIMETERC,V_CURRENT);
gw.present(ID_S_MULTIMETERC1,V_CURRENT);
pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT_PULLUP); // Set buttonPin as input and turn on internal pull up resistor
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set ledPin as output
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Make sure ledPin is off
// ------ load offset for current sensor
int validCheck = gw.loadState(0);
if (validCheck == 120){ // check to see if valid data exists
VQ = gw.loadState(1); // Load count offset into VQ
// Serial.print(" positive VQ offset loaded..."); Serial.println(VQ);
}
else if (validCheck == 125) {
VQ = -abs(gw.loadState(1));
// Serial.print(" negative VQ offset loaded..."); Serial.println(VQ);
}
else {
// Serial.println("VQ offset not set");
}
delay(500);
}
void loop()
{
buttonState = digitalRead(buttonPin);
//Serial.print("buttonstate..."); Serial.println(buttonState);
if (buttonState == LOW) {
VQ = determineVQ(ACSPin); //Returns the offset count needed to show zero with no load
if (VQ >= 0 && VQ < 255) { //check for valid data. VQ is positive number
gw.saveState(0, 120); // Store 120 value in eeprom position 0. use this to check for valid data at boot
gw.saveState(1, VQ); // Store offset count in eeprom. in case of re-boot
}
else if (VQ < 0 && VQ > -255) { // VQ is a negative number. negatives cannot be stored in eeprom
gw.saveState(0, 125); // Store 125 value in eeprom position 0. use this to check for valid data at boot
gw.saveState(1, abs(VQ)); // convert VQ to positive and Store offset count in eeprom. in case of re-boot
}
}
// ------------------ Start voltage readings --------------------
sample_count = 0;
sum = 0;
while (sample_count < NUM_SAMPLES) { // take a number of voltage samples
sum += analogRead(voltagePin);
sample_count++;
delay(10);
}
//Serial.print("sum count..."); Serial.println((sum / NUM_SAMPLES)); // print the count result. will be between 0 and 1023
int voltageI = map(sum/NUM_SAMPLES,0,1023,0,voltSenseMax); // map the reading and get our result in millivolts
//Serial.print("mapped volts..."); Serial.println(voltageI / 1000.0, 1); // convert millivolts back to volts and print. the 1 at the end determines how many decimal places to show
if ( voltageI != lastVoltage) { // check if we have a new value. only send data if it is different
gw.send(msg_S_MULTIMETERv.set(voltageI / 1000.0, 1)); // voltagel is in millivolts so we divide by 1000 to convert back to volts and
// send voltage message to gateway with 1 decimal place
lastVoltage = voltageI; // copy the current voltage reading for testing on the next loop
}
//--------------------Start Current readings---------------------------------
int milli = readCurrent(ACSPin); // take a reading from the ACS712 and send to the readcurrent function
//Serial.print("Milliamps..."); Serial.println(milli); // print the value (in milliamps) returned
if ( milli != lastmilli) // check if value has changed
{
if ( milli > 0) // Battery is charging
{
gw.send(msg_S_MULTIMETERc.set(milli/1000.0, 1)); // Send new data to charging amp device
gw.send(msg_S_MULTIMETERc1.set(0)); // set the dis-charging amp device to zero
lastmilli = milli;
}
else if (milli < 0) // Battery is discharging
{
gw.send(msg_S_MULTIMETERc.set(0)); // set the charging amp device to zero
gw.send(msg_S_MULTIMETERc1.set(abs(milli)/1000.0, 1)); // use abs(milli) to Send a positive number to dis-charging amp device
lastmilli = milli;
}
else // No current flowing, set both to zero
{
gw.send(msg_S_MULTIMETERc.set(0));
gw.send(msg_S_MULTIMETERc1.set(0));
lastmilli = milli;
}
}
//----------------------Teperature readings start------------------------
Serial.println(" Requesting temperatures...");
// Fetch temperatures from Dallas sensors
sensors.requestTemperatures(); // call sensors.requestTemperatures() to issue a global temperature request to all devices on the bus
// ------- query conversion time and sleep until conversion completed ------
int16_t conversionTime = sensors.millisToWaitForConversion(sensors.getResolution());
gw.sleep(conversionTime);
for (int i=0; i<2; i++) {
// Serial.print("Temperature for Device: ");Serial.print(i);Serial.print(" is: ");
// Serial.println(sensors.getTempCByIndex(i)); // Why "byIndex"?
// You can have more than one IC on the same bus.
// 0 refers to the first IC on the wire
float temperature = static_cast<float>(static_cast<int>((sensors.getTempCByIndex(i)) * 10.)) / 10.; // Fetch and round temperature to one decimal in celcius
if (lastTemperature[i] != temperature) // check for a changed temperature reading
{
gw.send(msg.setSensor(i).set(temperature,1)); // Send in the new temperature
lastTemperature[i]=temperature; // Save new temperatures for next compare
}
}
gw.sleep(SLEEP_TIME);
}
/*-------------- Function to get the offset required for ACS712 to show zero with no current flowing -----------------*/
int determineVQ(int PIN)
{
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn on LED to indicate offset being calculated
delay(500); // Delay to hold LED on
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn off LED
delay(150); // Delay to let readings stabilise
// Serial.print("estimating avg. quiscent voltage:");
long acsCount = 0;
for (int i=0; i<5000; i++) //read 5000 samples to stabilise value
{
acsCount += analogRead(PIN); // read the count value between 0 and 1023 and add it to acsCount
delay(1);
}
acsCount /= 5000; // acsCount now eaquals the average of the 5000 readings taken
// Serial.print(map(acsCount, 0, 1023, 0, 5000));Serial.println(" mV"); //Print the avg in millivolts
// Serial.print("acsCount:");Serial.println(acsCount); //Print the actual count value
return int(acsCount - 512); // return the count difference. 512 is the count for 2.5v which is what the reading should be with no current flow
}
/*--------------- Function to read current flowing ------------------*/
int readCurrent(int PIN)
{
int count = 0;
for (int i=0; i<5; i++) //read 5 analog count samples to stabilise value
{
count += analogRead(PIN) - VQ; //subtract the offset count VQ to improve accuracy
delay(1);
// Serial.print("raw count..."); Serial.println(count);
}
/* Notes on the conversion below
* .00488 is the volt value per count of the arduino adc. The analog pin measures from 0 to 5 volt and then assigns the result to
* a count from 0 to 1023, thats 1024 counts including zero. If we devide 5v by 1024 we get .oo488 volts for each count.
*
* The (count/5) just gets us the average of our 5 count samples.
*
* So after the first part of the equation (.00488 * (count/5) is complete we have converted our count reading into volts.
*
* The ACS712 can measure current flow in both directions so it outputs a voltage of 2.5v as it's center point (when no current is flowing).
* To allow for this offset we must subtract the 2.5v to center our voltage reading.
*
* Thats what the next part does (.00488 * (count/5)) - 2.5) After this is complete we are left with either a negative or positive voltage
* reading or a reading of zero for no current flow.
*
* NOTE: While the ACS712 is a 5v device it does not use the full 0 to 5v for it's output. The datasheet shows the 20A version has a sensitivity of
* 100mv per amp, so if we multiply 100mv by 20 we get 2v. That means the 20A ACS712 has an output range from .5v to 4.5v.
*
* So to convert our reading in volts to a reading in amps we need to add the last part ((.00488 * (count/5)) - 2.5)/(sensitivity/1000).
* The variable sensitivity is defined at the begining of the sketch and holds the ACS712 sensitvity amount, it is stored in millivolts.
* That is 66mv for the 30amp, 100mv for the 20amp and 185mv for the 5amp. As sensitivity is in millivolts we need to devide it by 1000
* to convert it back to volts so we can use it in the equation.
*
* Now we have our Amps value stored in the float amps. Integers are much easier to work with when checking for zero so we multiply by 1000
* to convert it to milliamps and return it as an integer.
*/
//Serial.print("VQ = ..."); Serial.println(VQ);
//Serial.print("current count..."); Serial.println(count/5);
//Serial.print("map milliamps..."); Serial.println(map((count/5), 102, 922, -20000, 20000));
float amps = ((.00488 * (count/5)) - 2.5) / (sensitivity/1000);
// Serial.print("float amps..."); Serial.println(amps, 1);
return int (amps * 1000); // convert to milliamps and return as an integer
}
Voltage Sensor:
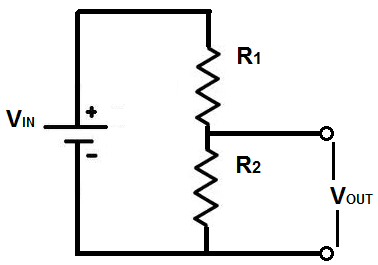
If you are not using a voltage sensor module you will need to construct a voltage divider circuit to measure the battery voltage. The reason for this is the Arduino Nano can only tolerate a maximum of 5v on its analog inputs so if we were to connect the 12v battery directly to the input we would most likely destroy the Arduino. A google search will turn up plenty of online voltage divider calculators to help you decide on the correct resistor values.
Make sure you choose an input voltage level for your divider that is well over the maximum of the voltage you intend to measure.
Our 12v system is likely to see voltages as high as 14.5v to 15v when charging and perhaps even higher if something has gone wrong so a divider with an input voltage of 25 to 30 volts would be a good choice. So for example if we were to use a combination of a 30k for R1 and 7.5k for R2 an input of 25v would result in an output of 5v.
You will need to change the value in the sketch code int voltSenseMax = 25000; to represent the input voltage in millivolts of your divider
I am using millivolts as I use the map function for the conversion later in the sketch, so integers are required. A typical voltage divider circuit is shown below.
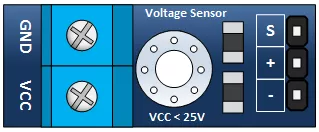
If you are using the voltage sensor module that I have used you will notice it has three terminals on the output side, the one marked with a + symbol is not used, I am not sure why it is even there.
DS18b20 Temperature Sensors:
These devices can be used with just two wires but I have used three as it seems this works best in noisy environments. The big advantage of these “one wire” devices is you can have more than one connected to the same input pin on the Arduino. The only requirement is one 4.7k pull-up resistor connected between VDD and DQ. The code I have used is based on the MySensors Dallas Temperature example.
ACS712 Current Sensing Module:
First be aware that the pin out can vary on these modules so check before you connect up. You can see in the picture below that the VCC and GND pins are reversed on these two.
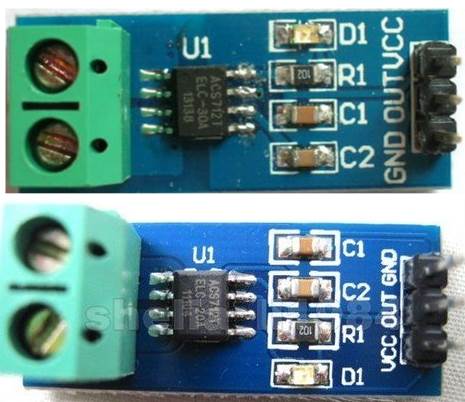
The ACS712 current sensing module is a 5v device that measures current flow and returns a voltage that can be used to determine the amount of current flowing. It is available in three versions 5A, 20A and 30A .
Importantly for this application they read current flow in both directions. To do this they output 2.5v when no current is flowing and increase or decrease the voltage depending on which direction the current is flowing.
None of them use the full 0 to 5v range for their output, the 20A version I have used has a sensitivity value of 100mv per 1A of current flow. As this is a 20A device we can multiply the 100mv by 20 and we get 2000mv or a 2v change for 20amps. We know the ACS712 shows an output of 2.5v when no current is flowing so using the 2v we now have the output range from .5v to 4.5v.
To use this device then we need a way to convert its voltage output to a measurement in amps.
Here is the basic equation needed
amps = ((voltsPerCount * count) – offsetVolts) / sensitivityVolts
Where
VoltsPerCount is the volt value per count of the Arduino ADC. The ADC measures the voltage present at the analog pin (0 to 5 volt) and then assigns the result as a count from 0 to 1023, that's 1024 counts including zero. If we divide 5v by 1024 we get .00488 volts for each count. So VoltsPerCount = .00488 Volts
count is the value our Arduino ADC returns after processing the output from the ACS712.
So after the first part of the equation (.00488 * (count) is complete we have converted our count reading from the arduino into volts.
The ACS712 can measure current flow in both directions so it outputs a voltage of 2.5v as it's center point (when no current is flowing). To allow for this offset we must subtract the 2.5v to center a 2.5 voltage reading at zero. So offsetVolts = 2.5 Volts
That's what the next part does ((.00488 * (count)) - 2.5) After this is complete we are left with a negative or positive voltage for current flowing in either direction or a value of zero for no current flow.
The sensitivity values for the ACS712 are shown on the datasheet as
185mv per Amp for the 5A
100mv per Amp for the 20A
66mv per Amp for the 30A
So to convert our value in volts to a value in amps we need to add the last part
((.00488 * (count)) – 2.5)/sensitivityVolts
Where sensitivityVolts equals the sensitivity value in volts for the device you are using. In my case the 20A version 100mv = .1 volts
amps = ((.00488 * (count)) – 2.5) / .1
Another way to do this would be to use the Arduino map function
we worked out earlier that the 20A version would output in the range from .5 to 4.5 volts, to convert that to count values we need to divide by .00488 .
Which gives us .5 / .00488 = 102 and 4.5 / .00488 = 922. map can only work with integers so it is best to use milliamps instead of amps for the output result.
The Arduino code for the 20A ACS712 would be:
milliamps = map(count, 102, 922, -20000, 20000);
Both of the above methods give very close results so you could use either. I have used the first method as it is easier to select the version of ACS712 you are using by changing the sensitivity.
The ACS712 is a hall effect device so it can be affected by stray magnetic fields that are nearby. It is best to locate it as far away as possible from any magnetic source to ensure you are getting a true reading. In use I found this was sometimes hard to achieve so I have added code to zero the reading if required. To do this I have used a push button and LED. If you are getting a constant current reading when no current is flowing simply push and hold the button until the led flashes. The sketch will then work out the offset required and apply that to zero the reading. This offset amount will then be saved to the Arduino EEPROM and will be reloaded and used even if the arduino is reset.
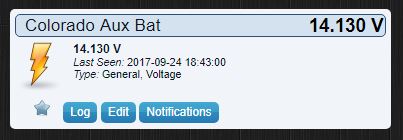
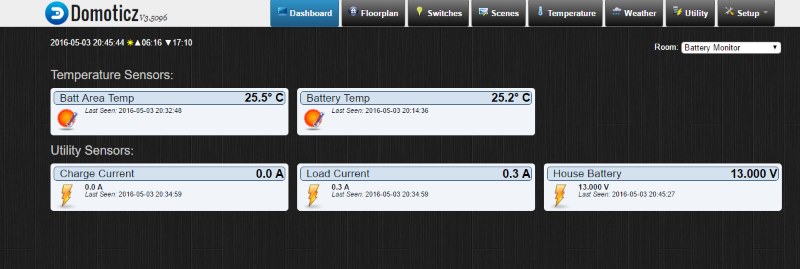
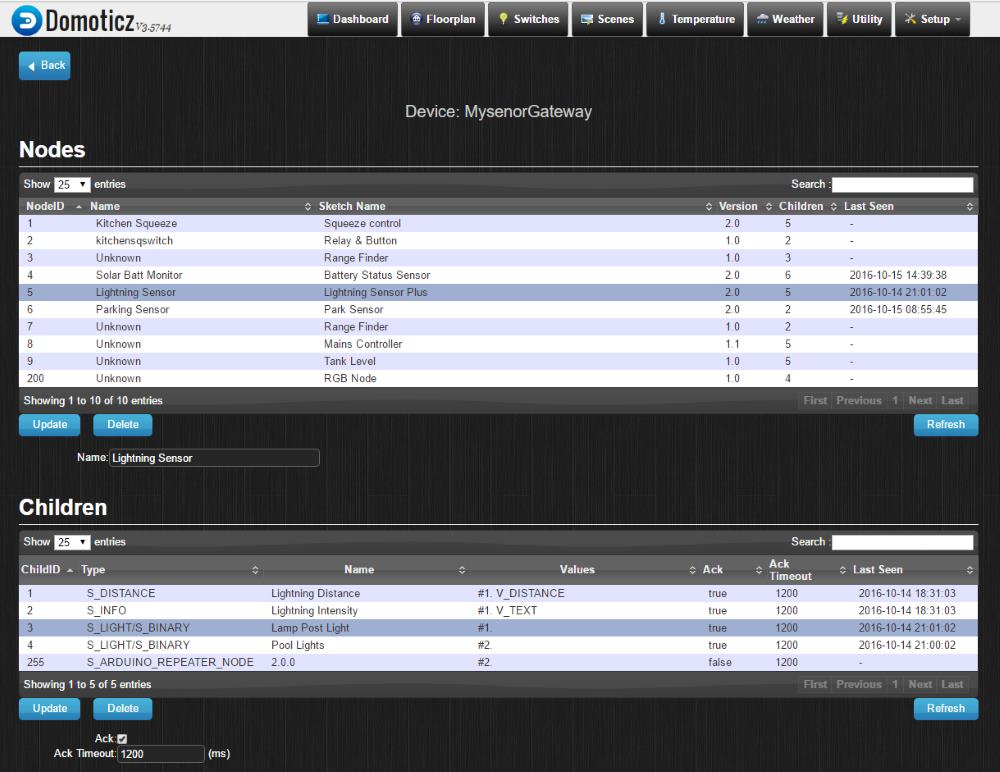
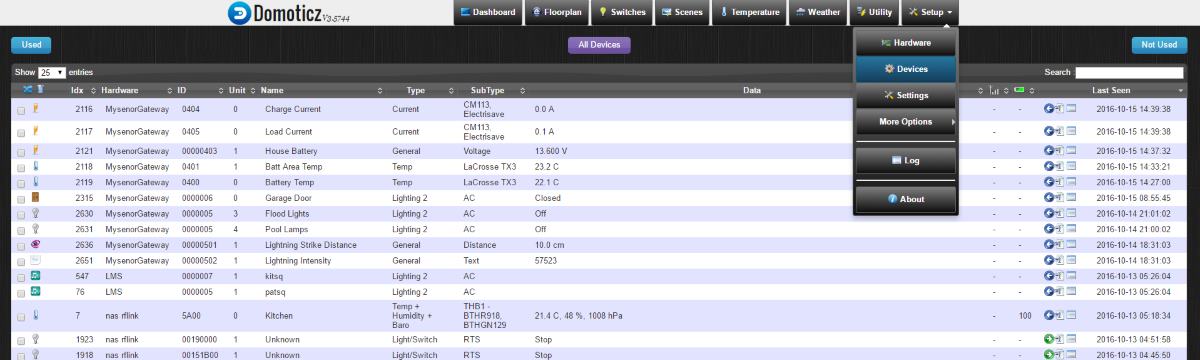
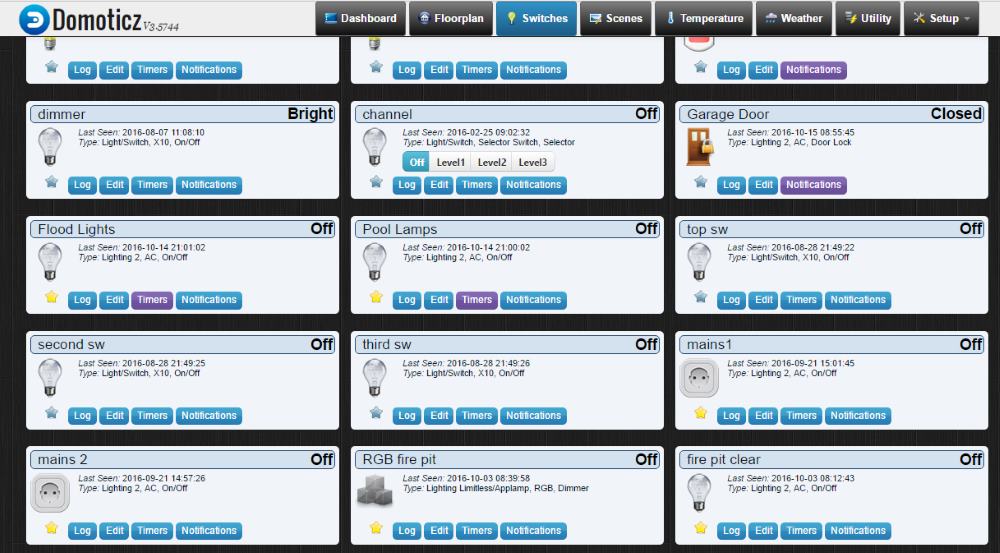
I am using Domoticz as my controller, here is what the end result looks like.